نص قرار تقسيم فلسطين رقم 181 باللغتين العربية والانجليزية
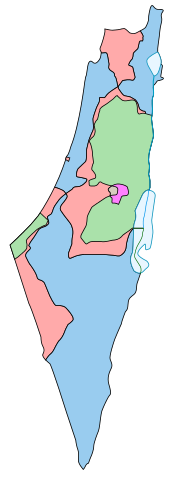 الحدود المحددة في خطة الأمم المتحدة للتقسيم لعام 1947::
الحدود المحددة في خطة الأمم المتحدة للتقسيم لعام 1947::
الهدنة خطوط ترسيم الحدود لعام 1949:
أمد/ قرار تقسيم فلسطين هو الاسم الذي أطلق على قرار الجمعية العامة التابعة لهيئة الأمم المتحدة رقم 181 والذي أُصدر بتاريخ 29 نوفمبر 1947 بعد التصويت (33 مع، 13 ضد، 10 ممتنع) ويتبنّى خطة تقسيم فلسطين القاضية بإنهاء الانتداب البريطاني على فلسطين وتقسيم أراضيها إلى 3 كيانات جديدة، كالتالي: 1. دولة عربية: وتقع على الجليل الغربي، ومدينة عكا، والضفة الغربية، والساحل الجنوبي الممتد من شمال مدينة أسدود وجنوبا حتى رفح، مع جزء من الصحراء على طول الشريط الحدودي مع مصر. 2. دولة يهودية: على السهل الساحلي من حيفا وحتى جنوب تل أبيب، والجليل الشرقي بما في ذلك بحيرة طبريا وإصبع الجليل، والنقب بما في ذلك أم الرشراش أو ما يعرف بإيلات حاليا. 3. القدس وبيت لحم والاراضي المجاورة، تحت وصاية دولية.
كان هذا القرار من أول محاولات الأمم المتحدة لحل النزاع العربي اليهودي على أرض فلسطين.
نص قرار تقسيم فلسطين رقم 181
(أ)
إن الجمعية العامة..
وقد عقدت دورة استثنائية بناء على طلب السلطة المنتدبة لتأليف لجنة خاصة وتكليفها الإعداد للنظر في مسألة حكومة فلسطين المستقلة في الدورة العادية الثانية..
وقد ألفت لجنة خاصة، وكلفتها التحقيق في جميع المسائل والقضايا المتعلقة بقضية فلسطين، وإعداد اقتراحات لحل المشكلة..
وقد تلقت وبحثت في تقرير اللجنة الخاصة بما في ذلك عدد من التوصيات الاجتماعية ومشروع تقسيم مع اتحاد اقتصادي أقرته أكثرية اللجنة الخاصة..
تعتبر أن من شأن الوضع الحالي في فلسطين إيقاع الضرر بالمصلحة العامة والعلاقات الودية بين الأمم.
تأخذ علما بتصريح سلطة الانتداب بأنها تسعى لإتمام جلائها عن فلسطين في 1 أغسطس/ آب 1948.
توصي المملكة المتحدة بصفتها السلطة المنتدبة على فلسطين، وجميع أعضاء الأمم المتحدة الآخرين، فيما يتعلق بحكومة فلسطين المستقلة، بتبني مشروع التقسيم والاتحاد الاقتصادي المرسوم أدناه وتنفيذه
وتطلب:
أ- أن يتخذ مجلس الأمن الإجراءات الضرورية، كما هي مبينة في الخطة، من أجل تنفيذها.
ب- أن ينظر مجلس الأمن -إذا كانت الظروف خلال الفترة الانتقالية تقتضي مثل ذلك النظر- فيما إذا كان الوضع في فلسطين يشكل تهديدا للسلم. فإذا قرر مجلس الأمن وجود مثل هذا التهديد وجب عليه في سبيل المحافظة على السلم والأمن الدوليين، أن يضيف إلى تفويض الجمعية العامة اتخاذ إجراءات تمنح لجنة الأمم المتحدة -تمشيا مع المادتين 39 و41 من الميثاق وكما هو مبين في هذا القرار- سلطة الاضطلاع في فلسطين بالمهمات المنوطة بها في هذا القرار.
ج- أن يعتبر مجلس الأمن كل محاولة لتغيير التسوية التي ينطوي عليها هذا القرار بالقوة تهديدا للسلام، أو خرقا له، أو عملا عدوانيا، وذلك بحسب المادة 39 من الميثاق.
د- أن يبلغ مجلس الوصاية بمسؤولياته التي تنطوي عليها هذه الخطة.
تدعو سكان فلسطين إلى القيام من جانبهم بالخطوات اللازمة لتحقيق هذه الخطة.
تناشد جميع الحكومات والشعوب أن تحجم عن القيام بأي عمل يحتمل أن يعيق هذه التوصيات أو يؤخر تنفيذها.
تفوض الأمين العام تغطية نفقات السفر والمعيشة لأعضاء اللجنة المشار إليها في الجزء الأول، القسم ب، الفقرة 1 أدناه، وذلك بناء على الأساس والصورة اللذين يراهما ملائمين في هذه الظروف، وتزويد اللجنة بالموظفين اللازمين للمساعدة على الاضطلاع بالمهمات التي عينتها الجمعية العامة له
(ب)
إن الجمعية العامة
تفوض الأمين العام سحب مبلغ من صندوق رأس المال العامل لا يتجاوز مليوني دولار للأغراض المبينة في الفقرة الأخيرة من القرار المتعلق بحكومة فلسطين المستقلة.
خطة التقسيم مع الاتحاد الاقتصادي
الجزء الأول: دستور فلسطين وحكومتها المستقلة
(أ) إنهاء الانتداب: التقسيم والاستقلال
ينتهي الانتداب على فلسطين في أقرب وقت ممكن، على ألا يتأخر في أي حال عن 1 أغسطس/ آب 1948.
يجب أن تجلو القوات المسلحة التابعة للسلطة المنتدبة عن فلسطين بالتدريج، ويتم الانسحاب في أقرب وقت ممكن على ألا يتأخر في أي حال عن 1 أغسطس/ آب 1948.
يجب أن تعلم السلطة المنتدبة اللجنة في أبكر وقت ممكن بنيتها إنهاء الانتداب والجلاء عن كل منطقة.
تبذل السلطة المنتدبة أفضل مساعيها لضمان الجلاء عن منطقة واقعة في أراضي الدولة اليهودية تضم ميناء بحريا وأرضا خلفية كافيين لتوفير تسهيلات لهجرة كبيرة، وذلك في أبكر موعد ممكن، على ألا يتأخر في أي حال عن 1 فبراير/ شباط 1948.
تنشأ في فلسطين الدولتان المستقلتان العربية واليهودية، والحكم الدولي الخاص بمدينة القدس المبين في الجزء الثالث من هذه الخطة، وذلك بعد شهرين من إتمام جلاء القوات المسلحة التابعة للسلطة المنتدبة، على ألا يتأخر ذلك في أي حال عن 1 أكتوبر/ تشرين الأول 1948. أما حدود الدولة العربية والدولة اليهودية ومدينة القدس فتكون كما وضعت في الجزأين الثاني والثالث أدناه.
تكون الفترة بين تبني الجمعية العامة توصيتها بشأن مسألة فلسطين وتوطيد استقلال الدولتين العربية واليهودية، فترة انتقالية.
(ب) خطوات تمهيدية للاستقلال
تؤلف لجنة مكونة من ممثل واحد لكل دولة من خمس دول أعضاء. وتنتخب الجمعية العامة الأعضاء الممثلين في اللجنة على أوسع أساس ممكن، جغرافيا وغير جغرافي.
في الوقت الذي تسحب فيه السلطة المنتدبة قواتها المسلحة، تسلم إدارة فلسطين بالتدريج إلى اللجنة التي ستعمل وفق توصيات الجمعية العامة بتوجيه مجلس الأمن. وعلى السلطة المنتدبة أن تنسق إلى أبعد حد ممكن خططها للانسحاب مع خطط اللجنة لتسلم المناطق التي يتم الجلاء عنها وإدارتها.
في سبيل تنفيذ هذه المسؤولية الإدارية تخول اللجنة سلطة إصدار الأنظمة الضرورية واتخاذ الإجراءات الأخرى كما يقتضي الحال.
- على السلطة المنتدبة ألا تقوم بأي عمل يحول دون تنفيذ اللجنة للإجراءات التي أوصت بها الجمعية العامة، أو يعرقله، أو يؤخره.
تمضي اللجنة لدى وصولها إلى فلسطين في تنفيذ الإجراءات لإقامة حدود الدولتين العربية واليهودية ومدينة القدس بحسب الخطوط العامة لتوصيات الجمعية العامة بشأن تقسيم فلسطين. على أن الحدود الموصوفة في الجزء الثاني من هذه الخطة يجب تعديلها كقاعدة بحيث لا تقسم حدود الدولة مناطق القرى ما لم تقتض ذلك أسباب ملحة.
تختار اللجنة وتنشئ في كل دولة بأسرع ما يمكن، بعد التشاور مع الأحزاب الديمقراطية والمنظمات العامة الأخرى في الدولتين العربية واليهودية، مجلس حكومة مؤقتا، وتسير أعمال مجلسي الحكومة المؤقتين العربي واليهودي بتوجيه اللجنة العام.
إذا لم يكن في الإمكان اختيار مجلس حكومة مؤقت لأي من الدولتين في 1 أبريل/ نيسان 1948، أو إذا انتخب (المجلس) ولم يستطع الاضطلاع بمهماته، فعلى اللجنة أن تبلغ مجلس الأمن بالأمر ليتخذ إزاء هذه الدولة التدابير التي يراها ملائمة، كما تبلغ الأمين العام به كي يحيط أعضاء الأمم المتحدة علما بذلك.
مع مراعاة نصوص هذه التوصيات، يكون لكل من المجلسين في أثناء فترة الانتقال -بإشراف اللجنة- كامل السلطة في المناطق التابعة لها، وبنوع خاص السلطة في القضايا المتعلقة بالهجرة وتنظيم الأراضي.
يتسلم بالتدريج كل من المجلسين المؤقتين في كل دولة من اللجنة التي يعملان تحت إشرافها، كامل التبعات الإدارية لكل منهما خلال الفترة التي تنقضي بين إنهاء الانتداب وتثبيت استقلال الدولة.
توعز اللجنة إلى مجلسي الحكومة المؤقتين لكل من الدولتين العربية واليهودية بعد تكوينهما، المضي في إنشاء أجهزة الحكومة الإدارية المركزية منها والمحلية.
يجند مجلس الحكومة المؤقت لكل دولة -في أقصر وقت ممكن- مليشيا مسلحة من سكان تلك الدولة تكون كافية في عددها للمحافظة على النظام الداخلي، وللحيلولة دون اشتباكات على الحدود.
يجب أن تكون هذه المليشيا المسلحة في كل دولة -من أجل أغراض العمليات- تحت إمرة ضباط يهود أو عرب مقيمين في تلك الدولة. بيد أن السيطرة السياسية والعسكرية العامة على المليشيا بما فيها اختيار قيادتها العليا، يجب أن تمارسها اللجنة.
يجري مجلس الحكومة المؤقت لكل دولة انتخابات "الجمعية التأسيسية" على أسس ديمقراطية، بحيث لا يتأخر ذلك عن شهرين اثنين من انسحاب القوات المسلحة التابعة للسلطة المنتدبة.
يضع مجلس الحكومة المؤقت أنظمة الانتخاب في كل دولة، وتوافق عليها اللجنة. ويكون مؤهلا لهذا الانتخاب في كل دولة من تجاوزت سنهم 18 عاما، على أن يكونوا (أ) مواطنين فلسطينيين مقيمين في تلك الدولة، و(ب) عربا ويهودا مقيمين في الدولة، وإن لم يكونوا مواطنين فلسطينيين ولكنهم وقعوا قبل الاقتراع بيانا أعربوا فيه عن نيتهم أن يصبحوا مواطنين في تلك الدولة.
يحق للعرب واليهود المقيمين في مدينة القدس ممن وقعوا بيانا أعربوا فيه عن نيتهم أن يصبحوا مواطنين، والعرب في الدولة العربية واليهود في الدولة اليهودية، أن يقترعوا في الدولتين العربية واليهودية بالترتيب المذكور.
يمكن للنساء أن يقترعن وأن ينتخبن للجمعية التأسيسية.
في أثناء الفترة الانتقالية لا يسمح ليهودي بأن يجعل إقامته في منطقة الدولة العربية المقترحة، ولا لعربي بأن يجعل إقامته في منطقة الدولة اليهودية المقترحة، إلا بإذن خاص من اللجنة.
تضع الجمعية التأسيسية لكل دولة مسودة دستور ديمقراطي، وتختار حكومة مؤقتة لتخلف مجلس الحكومة المؤقت الذي عينته اللجنة. ويضم دستورا الدولتين الفصلين الأول والثاني من التصريح المذكور في القسم (ج) أدناه، ويحويان في جملة ما يحويان، أحكاما لما يلي:
أ- تأسيس هيئة تشريعية في كل دولة تنتخب بالتصويت العام وبالاقتراع السري على أساس التمثيل النسبي، وهيئة تنفيذية مسؤولة أمام الهيئة التشريعية.
ب- تسوية جميع الخلافات الدولية التي قد تصبح الدولة طرفا فيها بالوسائل السلمية وبطريقة لا تعرض السلام والأمن والعدل الدولي للخطر.
ج- قبول التزام الدولة بالامتناع في علاقاتها الدولية من التهديد بالقوة أو استعمالها ضد الوحدة الإقليمية والاستقلال السياسي لأية دولة، أو بأية وسيلة أخرى تناقض هدف الأمم المتحدة.
د- أن تكفل الدولة لكل شخص وبغير تمييز حقوقا متساوية في الشؤون الدينية والمدنية والاقتصادية، والتمتع بحقوق الإنسان وبالحريات الأساسية، بما في ذلك حرية العبادة، وحرية استعمال اللغة التي يريدها، وحرية الخطابة والنشر والتعليم وعقد الاجتماعات وإنشاء الجمعيات.
هـ- المحافظة على حرية المرور والزيارة لجميع سكان ومواطني الدولة الأخرى في فلسطين ومدينة القدس، ويخضع ذلك لاعتبارات الأمن القومي، على أن تضبط كل دولة الإقامة ضمن حدودها.
تعين اللجنة لجنة اقتصادية تحضيرية من ثلاثة أعضاء لوضع ما يمكن من ترتيبات للتعاون الاقتصادي، بغية إنشاء الاتحاد الاقتصادي والمجلس الاقتصادي المشترك، كما هو مبين في القسم (د) أدناه، وذلك في أسرع وقت ممكن.
في أثناء الفترة ما بين تبني الجمعية العامة التوصيات المتعلقة بمسألة فلسطين وبين إنهاء الانتداب، تحتفظ السلطة المنتدبة في فلسطين بالمسؤولية التامة عن إدارة المناطق التي لم تسحب منها قوتها المسلحة، وتساعد اللجنة السلطة المنتدبة على تنفيذ مهماتها.
ولضمان استمرار الخدمات الإدارية، ولضمان انتقال الإدارة برمتها -لدى انسحاب القوات المسلحة للسلطة المنتدبة- إلى المجلسين المؤقتين والمجلس الاقتصادي المشترك بالترتيب، العاملة تحت إشراف اللجنة، يجب أن تنتقل بالتدريج -من السلطة المنتدبة إلى اللجنة- مسؤولية جميع مهمات الحكومة بما فيها المحافظة على القانون والنظام في المناطق التي انسحبت منها قوات الدولة المنتدبة.
تسترشد اللجنة في أعمالها بتوصيات الجمعية العامة، وبالتعليمات التي قد يرى مجلس الأمن ضرورة إصدارها.
تصبح الإجراءات التي تتخذها اللجنة -ضمن توصيات الجمعية العامة- نافذة فورا ما لم تكن اللجنة قد تسلمت قبل ذلك تعليمات مضادة من مجلس الأمن. وعلى اللجنة أن تقدم إلى مجلس الأمن تقريرا كل شهر عن حالة البلاد، أو أكثر من تقرير إذا كان ذلك مرغوبا فيه.
ترفع اللجنة تقريرها النهائي إلى الدورة العادية المقبلة للجمعية العامة، وإلى مجلس الأمن في الوقت نفسه.
(ج) تصريح
ترفع الحكومة المؤقتة في كل دولة مقترحة قبل الاستقلال تصريحاً إلى الأمم المتحدة يتضمن في جملة ما يتضمنه، النصوص التالية:
حكم عام
تعتبر الشروط التي يتضمنها التصريح قوانين أساسية للدولة، فلا يتعارض قانون أو نظام أو إجراء رسمي مع هذه الشروط أو يتدخل فيها، ولا يقدم عليها أي قانون أو نظام أو إجراء رسمي.
الفصل الأول
الأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية
لا تنكر أو تمس الحقوق القائمة المتعلقة بالأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية.
فيما يختص بالأماكن المقدسة، تضمن حرية الوصول والزيارة والمرور بما ينسجم مع الحقوق القائمة لجميع المقيمين والمواطنين في الدولة الأخرى وفي مدينة القدس، وكذلك للأجانب دون تمييز في الجنسية، على أن يخضع ذلك لمتطلبات الأمن القومي والنظام العام واللياقة. كذلك تضمن حرية العبادة بما ينسجم مع الحقوق القائمة، على أن يخضع ذلك لصيانة النظام العام واللياقة.
تصان الأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية، ولا يسمح بأي عمل يمكن أن يمس بطريقة من الطرق صفتها المقدسة. فإذا بدا للحكومة في أي وقت أن أي مكان مقدس أو مبنى أو موقع ديني معين بحاجة إلى ترميم عاجل، جاز للحكومة أن تدعو الطائفة أو الطوائف المعنية إلى إجراء الترميم. وإذا لم يتخذ إجراء خلال وقت معقول أمكن للحكومة أن تجريه بنفسها على نفقة الطائفة أو الطوائف المعنية.
لا تفرض ضريبة على أي مكان مقدس أو مبنى أو موقع ديني كان معفيا منها في تاريخ إنشاء الدولة.
يجب ألا يحدث أي تغيير في وقع هذه الضريبة يكون من شأنه التمييز بين مالكي أو قاطني الأماكن المقدسة أو الأبنية أو المواقع الدينية، أو يكون من شأنه وضع هؤلاء المالكين أو القاطنين في موضع أقل شأنا بالنسبة إلى الوقع العام للضريبة مما كان عليه حالهم وقت تبني توصيات الجمعية.
يكون لحاكم مدينة القدس الحق في تقرير ما إذا كانت أحكام دستور الدولة، المتعلقة بالأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية ضمن حدود الدولة والحقوق الدينية المختصة بها، تطبق وتحترم بصورة صحيحة، وله أن يثبت على أساس الحقوق القائمة، الخلافات التي قد تنشب بين الطوائف الدينية المختلفة، أو من طقوس طائفة دينية واحدة بالنسبة إلى هذه الأماكن والأبنية والمواقع. ويجب أن يلقى الحاكم تعاونا تاما ويتمتع بالامتيازات والحصانات الضرورية للاضطلاع بمهماته في الدولة.
الفصل الثاني
الحقوق الدينية وحقوق الأقليات
تكون حرية العقيدة والممارسة الحرة لجميع طقوس العبادة المتفقة مع النظام العام والآداب الحسنة مضمونة للجميع.
لا يجوز التمييز بين السكان بأي شكل من الأشكال بسبب الأصل أو الدين أو اللغة أو الجنس.
يكون لجميع الأشخاص الخاضعين لولاية الدولة الحق في حماية القانون.
يجب احترام القانون العائلي، والأحوال الشخصية لمختلف الأقليات، وكذلك مصالحها الدينية بما في ذلك الأوقاف.
باستثناء ما يتطلبه حفظ النظام وحسن الإدارة لن يتخذ أي تدبير من شأنه أن يعيق أو يتدخل في نشاط المؤسسات الدينية أو الخبرات لجميع المذاهب، أو يجحف بحقوق أي ممثل لهذه المؤسسات أو عضو فيها بسبب الدين أو القومية.
تؤمن الدولة للأقلية العربية أو اليهودية القدر الكافي من التعليم الابتدائي والثانوي بلغتها، ووفق تقاليدها الثقافية.
ولن ينكر حق كل طائفة في الاحتفاظ بمدارسها لتعليم أبنائها بلغتها الخاصة ما دامت تلتزم بمقتضيات التعليم العامة التي قد تفرضها الدولة. أما مؤسسات التعليم الأجنبية فتداوم على نشاطها على أساس حقوقها القائمة.
لن تفرض أية قيود على حرية أي مواطن في استعمال أية لغة في المحادثات الخاصة أو في التجارة أو الدين أو الصحافة أو المنشورات على أنواعها أو في الاجتماعات العامة.
لا يجوز أن يسمح بنزع ملكية أي أرض تخص عربيا في الدولة اليهودية أو يهوديا في الدولة العربية إلا للمنفعة العامة. وفي جميع الحالات يجب دفع تعويض كامل وبالمقدار الذي تحدده المحكمة العليا، وأن يتم الدفع قبل تجريد المالك من أرضه.
الفصل الثالث
المواطنة والاتفاقيات الدولية والالتزامات المالية
1- المواطنة (Citizenship)
إن المواطنين الفلسطينيين المقيمين في فلسطين خارج مدينة القدس، والعرب واليهود المقيمين في فلسطين خارج مدينة القدس، وهم غير حائزين على الجنسية الفلسطينية يصبحون مواطنين في الدولة التي يقيمون فيها، ويتمتعون بالحقوق المدنية والسياسية جميعها بمجرد الاعتراف باستقلال الدولة. ويجوز لكل شخص تجاوز الثامنة عشرة من العمر خلال سنة من يوم الاعتراف باستقلال الدولة التي يقيم فيها، أن يختار جنسية الدولة الأخرى شرط ألا يكون لأي عربي يقيم في الإقليم العربي المقترح الحق في اختيار جنسية الدولة اليهودية المقترحة، وألا يكون لأي يهودي يقيم في الدولة اليهودية المقترحة الحق في اختيار جنسية الدولة العربية المقترحة. وكل شخص يمارس حق الاختيار هذا يعتبر أنه في الوقت ذاته قد أجرى الاختيار بالنسبة إلى زوجته وأولاده الذين هم دون الثامنة عشرة من العمر.
ويجوز للعرب المقيمين في إقليم الدولة اليهودية المقترحة ولليهود المقيمين في إقليم الدولة العربية المقترحة، الذين وقعوا تصريحا برغبتهم في اختيار جنسية الدولة الأخرى أن يشتركوا في انتخابات الجمعية التأسيسية لهذه الدولة، ولكن ليس في انتخابات الجمعية التأسيسية للدولة التي يقيمون فيها.
2- الاتفاقات الدولية
أ- تربط الدولة بجميع المعاهدات والاتفاقيات الدولية ذات الصفة العامة والخاصة التي قد أصبحت فلسطين طرفا فيها. وعلى الدولة أن تحترم هذه المعاهدات والاتفاقيات طوال المدة المقررة لها لمدى عقدها، مع عدم الإخلال بأي حق في الإنهاء قد تنص عليه هذه الاتفاقيات.
ب- كل نزاع بشأن إمكان تطبيق الاتفاقيات أو المعاهدات الدولية التي وقعتها أو انضمت إليها حكومة الانتداب نيابة عن فلسطين أو بشأن استمرار صحتها، يرفع إلى محكمة العدل الدولية وفق أحكام نظام المحكمة.
3- الالتزامات المالية
أ- على الدولة أن تحترم وتنفذ جميع أنواع الالتزامات المالية التي أخذتها الدولة المنتدبة على عاتقها نيابة عن فلسطين في أثناء ممارستها الانتداب والتي تعترف بها الدولة، وهذا الشرط يشمل حق الموظفين في مرتبات التقاعد والتعويضات والمكافآت.
ب- تفي الدولة عن طريق اشتراكها في المجلس الاقتصادي المختلط بتلك الفئة من الالتزامات التي تشمل عموم فلسطين، وتفي بصورة فردية بتلك التي يمكن التفاهم عليها وتوزيعها بالعدل بين الدولتين.
ج- يجب إنشاء "محكمة ادعاءات" (Court of Claims) تابعة للمجلس الاقتصادي المشترك، ومكونة من عضو تعينه منظمة الأمم المتحدة ومن ممثل للمملكة المتحدة وممثل للدولة ذات الشأن، ويرفع إلى هذه المحكمة كل نزاع بين المملكة المتحدة وهذه الدولة خاص بالمطالب غير المعترف بها من قبل هذه الأخيرة.
ج- تبقى الامتيازات التجارية الممنوحة بالنسبة إلى أي جزء من فلسطين قبل موافقة الجمعية العامة على القرار، صالحة وفق شروطها ما لم تعدل بطريق الاتفاق بين صاحب الامتياز والدولة.
الفصل الرابع
أحكام متنوعة
تضمن الأمم المتحدة أحكام الفصلين الأول والثاني من التصريح، ولا يجري عليها أي تعديل دون موافقة الجمعية العامة للأمم المتحدة. ويحق لأي عضو في الأمم المتحدة أن ينبه الجمعية العامة إلى أي خرق لهذه البنود أو إلى خطر خرقها. ويجوز للجمعية العامة بناء على ذلك أن توصي بما تراه ملائما للظروف.
يحال كل خلاف متعلق بتطبيق هذا التصريح أو تفسيره على محكمة العدل الدولية -بناء على طلب أحد الطرفين- ما لم يتفق الطرفان على أسلوب تسوية آخر.
(د) الاتحاد الاقتصادي والعبور
يشترك مجلس الحكومة المؤقت لكل دولة في وضع مشروع اتحاد اقتصادي وعبور (ترانزيت). وتحرر اللجنة المنصوص عليها في الفقرة 1 من القسم ب نص هذا المشروع منتفعة إلى أبعد مدى ممكن بمشورة ومعاونة المؤسسات والهيئات الممثلة لكل من الدولتين. ويجب أن يتضمن مسائل أخرى ذات نفع مشترك، وإن لم يتم اتفاق المجلسين الحكوميين المؤقتين على هذا المشروع حتى أول أبريل/ نيسان 1948 فإن اللجنة ستقوم بوضعه.
الاتحاد الاقتصادي الفلسطيني
تكون للاتحاد الاقتصادي الفلسطيني الأهداف التالية:
أ- إيجاد وحدة جمركية.
ب- إقامة نظام نقدي مشترك يتضمن سعر صرف واحدا.
ج- إدارة السكك الحديدية والطرق المشتركة بين الدولتين، ومرافق البريد والبرق والهاتف والموانئ والمطارات المستعملة في التجارة الدولية، على أساس من عدم التمييز في سبيل المصلحة العامة.
د- الإنماء الاقتصادي المشترك، وخصوصا فيما يتعلق بالري واستصلاح الأراضي وصيانة التربة.
هـ- تمكين الدولتين ومدينة القدس من الوصول إلى المياه ومصادر الطاقة على أساس من عدم التمييز.
ينشأ مجلس اقتصادي مشترك يتكون من ثلاثة ممثلين لكل من الدولتين، ومن ثلاثة أعضاء أجانب يعينهم المجلس الاقتصادي والاجتماعي لمنظمة الأمم المتحدة. ويعين الأعضاء الأجانب أول مرة لفترة ثلاث سنوات، ويمارسون وظائفهم بصفتهم الشخصية وليس كممثلين لدول.
تكون وظيفة المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك تنفيذ التدابير اللازمة لبلوغ أهداف الاتحاد الاقتصادي بطريقة مباشرة أو بالانتداب، ويفوض جميع سلطات التنظيم والإدارة اللازمة لأداء مهمته.
تتعهد الدولتان بتنفيذ قرار المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك، وتؤخذ قراراته بالأكثرية.
يجوز للمجلس في حال تقصير إحدى الدولتين في إجراء العمل اللازم أن يقرر بأكثرية ستة من أعضائه حبس جزء ملائم من الحصة التي تعود إلى الدولة المذكورة من عائدات الجمارك بموجب الاتحاد الاقتصادي، فإن تمادت الدولة في عدم التعاون يجوز للمجلس أن يقرر بالأكثرية البسيطة اتخاذ ما يراه ملائما من العقوبات بما في ذلك التصرف في الأموال التي يكون احتبسها.
تكون وظيفة المجلس -فيما يتعلق بالإنماء الاقتصادي- تخطيط برامج مشتركة بين الدولتين ودراستها وتشجيعها، ولكن لا يجوز له تنفيذ هذه المشاريع بغير موافقة الدولتين وموافقة مدينة القدس في حال تأثرها مباشرة بمشروع الإنماء.
فيما يتعلق بالنظام النقدي المشترك يكون إصدار العملات المتداولة في الدولتين وفي مدينة القدس تحت سلطة المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك الذي يكون سلطة الإصدار الوحيدة والذي يحدد الاحتياطي الذي يحتفظ به كضمان لهذه العملات.
يجوز لكل دولة -بما يتفق مع البند 2 (ب) أعلاه- أن تدير مصرفها المركزي الخاص، وأن تتحكم بسياستها المالية والائتمانية وبإيراداتها ونفقاتها من القطع الأجنبي، وبمنح رخص الاستيراد، وأن تقوم بعمليات مالية دولية اعتمادا على ائتمانها الذاتي. ويكون للمجلس الاقتصادي المشترك خلال السنتين التاليتين مباشرة لانتهاء الانتداب سلطة اتخاذ جميع ما قد يلزم من تدابير كي يكون متوفرا لكل دولة -في فترة مدتها اثنا عشر شهرا- مبلغ من القطع الأجنبي كاف لكي يضمن للإقليم ذاته مقدارا من البضائع والخدمات المستوردة لأجل الاستهلاك المحلي مساويا لمقدار من البضائع والخدمات التي استهلكها الإقليم خلال الاثني عشر شهرا المنتهية في 31 ديسمبر/ كانون الأول 1947، وذلك بالقدر الذي يسمح به مجموع الدخل من القطع الأجنبي الذي تحصل عليه الدولتان من تصدير البضائع والخدمات، وشرط أن تتخذ كل دولة التدابير الملائمة لصيانة مواردها الخاصة من القطع الأجنبي.
تتمتع كل دولة بجميع السلطات الاقتصادية غير الموكولة صراحة إلى المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك.
توضع تعريفة جمركية تترك حرية التجارة كاملة بين الدولتين، وكذلك بين الدولتين ومدينة القدس.
تضع جداول التعريفة لجنة خاصة للتعريفات مكونة من ممثلين متساوي العدد عن كل دولة من الدولتين، وتعرض على المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك للموافقة عليها بأكثرية الأصوات. وفي حال وقوع خلاف في لجنة التعريفة فإن المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك يقوم بالتوسط في النقاط المتنازع عليها، كما يضع التعريفة بنفسه في حال عدم توصل لجنة التعريفة إلى وضع جدول للتعريفة في المهلة المحددة.
يكون لتكاليف البنود التالية الأولوية من دخل الجمارك وغيرها من بنود الدخل العام للمجلس الاقتصادي المشترك:
أ- نفقات المصالح الجمركية ومصاريف إدارة المصالح المشتركة.
ب- نفقات إدارة المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك.
ج- الالتزامات المالية لإدارة فلسطين وهي:
أ- نفقات إدارة الدين العام.
ب- معاشات التقاعد التي تدفع حاليا أو التي ستدفع في المستقبل وفقا للقوانين وعلى النطاق المنصوص عليه في البند (3) من الفصل الثالث أعلاه.
بعد تغطية هذه الالتزامات بنمائها، يوزع فائض الدخل من الجمارك والخدمات المشتركة على الصورة التالية:
تمنح مدينة القدس مبلغا لا يقل عن 5% ولا يزيد على 10% ويوزع المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك الباقي بصورة عادلة على الدولتين هادفا المحافظة على مستوى معقول وملائم للخدمات الحكومية والاجتماعية في كلتا الدولتين، غير أنه لا يجوز أن تزيد حصة أي منهما على المقدار الذي ساهمت به في دخل الاتحاد الاقتصادي بأكثر من أربعة ملايين جنيه في السنة. ويجوز للمجلس الاقتصادي المشترك بعد انقضاء خمس سنوات أن يعيد النظر في مبادئ توزيع الإيرادات المشتركة مستلهما في ذلك اعتبارات العدالة.
تشترك الدولتان في عقد جميع الاتفاقيات والمعاهدات الدولية الخاصة بالتعريفات الجمركية، وبمرافق المواصلات الموضوعة تحت سلطة المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك، وتلزم الدولتان في هذه الأمور بأن تتصرفا طبقا لقرار أكثرية المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك.
يبذل المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك جهده ليوفر لصادرات فلسطين منفذا عادلا ومتساويا إلى الأسواق العالمية.
على جميع المشاريع المدارة من المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك أن تدفع أجورا عادلة على أساس واحد.
حرية المرور والزيارة: يتضمن التعهد أحكاما تحفظ حرية المرور والزيارة لجميع سكان أو مواطني كلتا الدولتين ومدينة القدس ضمن اعتبارات الأمن، على أن تضبط كل دولة ومدينة القدس الإقامة داخل حدودها.
إنهاء التعهد وتعديله وتغييره: يبقى التعهد وأية اتفاقية صادرة عنه نافذتين مدة عشر سنين، ويستمر كذلك حتى يطلب أي من الطرفين إنهاءه فينهى بعد ذلك بعامين.
لا يجوز خلال فترة السنوات العشر الأولى تعديل هذا التعهد أو أية اتفاقية صادرة عنه، إلا بقبول كلا الطرفين وموافقة الجمعية العامة.
كل نزاع متعلق بتطبيق أو تفسير التعهد وأية اتفاقية صادرة عنه يرجع فيه -بناء على طلب أي من الفريقين- إلى محكمة العدل الدولية، ما لم يتفق الطرفان على وسيلة أخرى للتسوية.
(هـ) الموجودات
توزع أموال إدارة فلسطين المنقولة بين الدولتين العربية واليهودية ومدينة القدس على أساس عادل، ويجب أن يجري التوزيع بواسطة لجنة الأمم المتحدة المذكورة في القسم (ب) بند (1) أعلاه، وتصبح الأموال غير المنقولة ملكا للحكومة التي توجد هذه الأموال في إقليمها.
يجب على الدولة المنتدبة خلال الفترة التي تنقضي بين تاريخ تعيين لجنة الأمم المتحدة وانتهاء الانتداب أن تتشاور مع اللجنة في أي إجراء تفكر في اتخاذه، متضمنا تصفية أموال حكومة فلسطين والتصرف بها أو رهنها، مثل فائض الخزينة المتراكم، وريع السندات التي أصدرتها الحكومة، وأراضي الدولة، وأية موجودات أخرى.
و- الدخول في عضوية الأمم المتحدة
عندما يصبح استقلال الدولة العربية أو اليهودية نافذاً -كما هو منصوص عليه في المشروع الحاضر- ويكون البيان والتعهد المنصوص عليهما في هذا المشروع قد وقعا من قبل الدولة، يصبح عندئذ من الملائم أن ينظر بعين العطف إلى طلب قبولها عضوا في الأمم المتحدة طبقا للمادة (4) من ميثاق الأمم المتحدة.
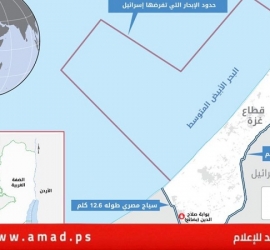
الجزء الثاني: الحدود
أ- الدولة العربية
يحد منطقة الدولة العربية في الجليل الغربي من الغرب البحر الأبيض المتوسط، ومن الشمال حدود لبنان من رأس الناقورة إلى نقطة شمالي الصالحة، ومن هناك يسير خط الحدود في اتجاه الجنوب تاركاً منطقة الصالحة المبنية في الدول العربية فيلاقي النقطة الواقعة في أقصى جنوبي هذه القرية. من ثم يتبع خط الحدود الغربية لقرى علما والريحانية طبطبه، ومنها يتبع خط الحد الشمالي لقرية ميرون فيلتقي بخط حدود قضاء عكا/ صفد. ويتبع هذا الخط إلى نقطة غربي قرية السموعي، ويلاقيه مرة أخرى في نقطة في أقصى شمالي قرية الفراضية. ومن هناك يتبع خط حدود القضاء إلى طريق عكا/ صفد العام، ومن هنا يتبع الحدود الغربية لقرية كفر عنان حتى يصل خط حدود قضاء طبريا/ عكا، مارا بغربي تقاطع عكا/ صفد ولوبية/ كفر عنان، ومن الزاوية الجنوبية الغربية لقرية كفر عنان يتبع خط الحدود الحدود الغربية لقضاء طبريا إلى نقطة قريبة من خط الحدود بين قريتي المغار وعيلبون، ومن ثم يبرز إلى الغرب ليضم أكبر مساحة من الجزء الشرقي من سهل البطوف لازمة للخزان الذي اقترحته الوكالة اليهودية لري الأراضي إلى الجنوب والشرق.
تعود الحدود فتلتقي بحدود قضاء طبريا في نقطة على طريق الناصرة/ طبريا إلى الجنوب الشرقي من منطقة طرعان المبنية، ومن هناك تسير في اتجاه الجنوب، تابعة بادئ الأمر حدود القضاء، ثم مارة بين مدرسة خضوري الزراعية وجبل تابور إلى نقطة في الجنوب عند قاعدة جبل تابور. ومن هنا تسير إلى الغرب، موازية لخط التقاطع العرضي 230 إلى الزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من أراضي قرية تل عداشيم. ثم تسير إلى الزاوية الشمالية الغربية من هذه الأراضي ومنها تنعطف إلى الجنوب والغرب حتى تضم إلى الدولة العربية مصادر مياه الناصرة في قرية يافا. وحين تصل جنجار، تتبع حدود أراضي هذه القرية الشرقية والشمالية والغربية إلى زاويتها الجنوبية الغربية، ومن هناك تسير في خط مستقيم إلى نقطة على سكة حديد حيفا/ العفولة على الحدود ما بين قريتي ساريد والمجيدل، وهذه هي نقطة التقاطع.
تتخذ الحدود الجنوبية الغربية من منطقة الدولة العربية في الجليل خطا من هذه النقطة مارا نحو الشمال على محاذاة حدود ساريد وغفات الشرقية إلى الزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من نهلال، ماضيا من هناك عبر أراضي كفار هاحوريش إلى نقطة متوسطة على الحدود الجنوبية لقرية عيلوط، ومن ثم نحو الغرب محاذيا حدود تلك القرية إلى حدود بيت لحم الشرقية، ومنها نحو الشمال فالشمال الشرقي على حدودها الغربية إلى الزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من ولدهايم، ومن هناك جنوب الشمال الغربي عبر أراضي قرية شفاعمرو إلى الزاوية الجنوبية الشرقية من رامات يوحانان. ومن هنا يسير شمالا فشمالا شرقيا إلى نقطة على طريق شفاعمرو/ حيفا، إلى الغرب من اتصالها بطريق عبلين. ومن هناك يسير شمالا شرقيا إلى نقطة على الحدود الجنوبية من طريق عبلين للبروة. ومن هناك يسير على تلك الحدود إلى أقصى نقطة غربية لها، ومنها ينعطف إلى الشمال فيمضي عبر أراضي قرية تمرة إلى أقصى زاوية شمالية غربية، وعلى محاذاة حدود جوليس الغربية حتى يصل إلى طريق عكا/ صفد. بعد ذلك يسير صوب الغرب حتى يصل إلى طريق عكا/ صفد إلى حدود منقطة الجليل/ حيفا، ومن هذه النقطة يتبع تلك الحدود إلى البحر.
تبدأ حدود منطقة السامرة واليهودية الجبلية على نهر الأردن في وادي المالح إلى الجنوب الشرقي من بيسان، وتسير نحو الغرب فتلتقي بطريق بيسان/ أريحا، ثم تتبع الجانب الغربي من ذلك الطريق في اتجاه شمالي غربي إلى ملتقى حدود أقضية بيسان ونابلس وجنين. ومن هذه النقطة تتبع حدود مقاطعة نابلس/ جنين في اتجاه الغرب إلى مسافة تبلغ نحو ثلاثة كيلومترات، ثم تنعطف نحو الشمال الغربي مارة بشرقي المنطقة المبنية من قرى جليون وفقوعة إلى حدود مقاطعتي جنين وبيسان في نقطة إلى الشمال الشرقي من نورس. ومن هنا تسير بادئ الأمر نحو الشمال الغربي إلى نقطة شمالي المنطقة المبنية من زرعين، ثم شطر الغرب إلى سكة حديد العفولة/ جنين، ومن ثم في اتجاه شمالي غربي على طول خط حدود المنطقة إلى نقطة التقاطع على الخط الحديدي الحجازي. من هنا تتجه الحدود إلى الجنوب الغربي بحيث تكون المنطقة المبنية وبعض أراضي خربة ليد ضمن الدولة العربية، ثم تقطع طريف حيفا/ جنين في نقطة على حدود المنطقة بين حيفا والسامرة إلى الغرب من المنسي، وتتبع هذه الحدود إلى أقصى نقطة جنوبي قرية البطيمات. ومن هنا تتبع الحدود الشمالية والشرقية لقرية عرعرة ملتقية مرة أخرى بخط حدود المنطقة بين حيفا والسامرة في وادي عارة، ومن هناك تتجه نحو الجنوب فالجنوب الغربي في خط مستقيم تقريبا ملتقية بحدود قاقون الغربية، ومتجهة معها إلى نقطة تقع إلى الشرق من سكة الحديد على حدود قرية قاقون الشرقية. ومن هنا تسير مع سكة الحديد مسافة إلى الشرق منها نحو نقطة تقع شرقي محطة سكة الحديد في طولكرم، ومن هناك تتبع الحدود خطا في منتصف المسافة بين سكة الحديد وبين طريق طولكرم/ قلقيلية/ جلجولية/ رأس العين حتى نقطة تقع شرقي محطة رأس العين، التي تسير منها في اتجاه سكة الحديد مسافة إلى الشرق حتى نقطة على سكة الحديد جنوبي ملتقى سكك حيفا/ اللد/ بيت نبالا، ومن هنا تسير في اتجاه حدود مطار اللد الجنوبية إلى زاويته الجنوبية الغربية، ومن ثم في اتجاه جنوبي غربي إلى نقطة المنطقة المبنية من صرفند العمار، ومن هناك تنعطف شطر الجنوب مارة غربي المنطقة المبنية من أبو الفضل إلى الزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من أراضي بير يعقوب (يجب تحديد خط الحدود بحيث يسمح باتصال مباشر بين الدولة العربية ومطار اللد)، ومن هناك يتبع خط الحدود حدود بلدة الرملة الغربية والجنوبية إلى الزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من قرية النعماني. ومن ثم يسير في خط مستقيم إلى نقطة في أقصى الجنوب من البرية على محاذاة حدود تلك القرية الشرقية وحدود قرية عنابة الجنوبية، ومن هناك ينعطف شمالا فيتبع الجانب الجنوبي من طريق يافا/ القدس حتى القباب، ومنها يتبع الطريق إلى حدود أبي شوشة، ويسير في محاذاة الحدود الشرقية لأبي شوشة وسيدون وحلدة حتى نقطة في أقصى الجنوب من حلدة. ويسير من هنا نحو الغرب في خط مستقيم إلى الزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من أم كلخا، ومنها يتبع الحدود الشمالية لأم كلخا والقزازة وحدود المخيزن الشمالية والغربية إلى حدود منطقة غزة، ومنها يسير عبر أراضي قريتي المسمية الكبيرة وياصور إلى النقطة الجنوبية من التقاطع الواقع في منتصف المسافة بين المناطق المبنية من ياصور وبطاني شرقي.
تتجه خطوط الحدود من نقطة التقاطع الجنوبية نحو الشمال الغربي بين قريتي غان يفنة وبرقة إلى البحر في نقطة تقع في منتصف المسافة بين النبي يونس وميناء القلاع، ونحو الجنوب الشرقي إلى نقطة غربي قسطينة، ومنها تنعطف في اتجاه جنوبي غربي مارة شرقي المناطق المبنية من السوافير وعبدس. ومن الزاوية الجنوبية الشرقية من قرية عبدس تسير إلى نقطة في الجنوب الشرقي من المنطقة المبنية من بيت عقة قاطعة طريق الخليل/ المجدل إلى الغرب من المنطقة المبنية من عراق سويدان، ومن هناك تسير في اتجاه جنوبي على محاذاة الحدود الغربية لقرية الفالوجة إلى حدود قضاء بئر السبع. ثم تسير عبر الأراضي القبلية لعرب الجبارات إلى نقطة على الحدود ما بين قضاءي بئر السبع إلى الشمال من خربة خويلفة، ومن هناك تسير في اتجاه جنوبي غربي إلى نقطة على طريق بئر السبع/ غزة العام على بعد كيلومترين إلى الشمال الغربي من البلدة ثم تنعطف شطر الجنوب الشرقي فتصل وادي السبع في نقطة واقعة على بعد كيلومتر واحد إلى الغرب منه. ومن هنا تنعطف في اتجاه شمالي شرقي، وتسير على محاذاة وادي السبع وعلى محاذاة طريق بئر السبع/ الخليل مسافة كيلومتر واحد، ومن ثم تنعطف شرقا وتسير في خط مستقيم إلى خربة كسيقة لتلتقي بحدود المقاطعة بين بئر السبع والخليل. ثم تتبع حدود بئر السبع/ الخليل في اتجاه الشرق إلى نقطة شمالي رأس الزويرة. ثم تنفصل عنها فتقطع قاعدة الفراغ من بين خطي الطول 150 و160.
وعلى بعد خمسة كيلومترات تقريبا إلى الشمال الشرقي من رأس الزويرة، تنعطف الحدود شمالا بحيث تستثني من الدولة العربية قطاعا على محاذاة ساحل البحر الميت لا يزيد عرضه على سبعة كيلومترات وذلك حتى عين جدي، حيث تنعطف من هناك إلى الشرق لتلتقي حدود شرق الأردن في البحر الميت.
تبدأ الحدود الشمالية للجزء العربي من السهل الساحلي من نقطة بين ميناء القلاع والنبي يونس، مارة بين المناطق المبنية من غان يفنة وبرقة حتى نقطة التقاطع، ومن هنا تسير في اتجاه الجنوب الغربي مارة عبر أراضي بطاني شرقي على محاذاة الحد الشرقي من أراضي بيت داراس وعبر أراضي جوليس، تاركة المناطق المبنية من بطاني شرقي وجوليس في الغرب، وماضية حتى الزاوية الشمالية الغربية من أراضي بيت طيما. ومن هناك تتجه إلى الشرق من الجية عبر أراضي قرية البربرة على محاذاة الحدود الشرقية من قرى بيت جرجا ودير سنيد ودمرة. ومن الزاوية الشرقية لدمرة تعبر حدود أراضي بيت حانون تاركة الأراضي اليهودية من نير عام صوب الشرق. ومن الزاوية الجنوبية الشرقية لبيت حانون تتجة الحدود إلى الجنوب الغربي نحو نقطة إلى الجنوب من خط التوازي 100، ثم تنعطف نحو الشمال الغربي مسافة كيلومترين، وتنعطف ثانية في اتجاه جنوبي غربي وتمضي في خط مستقيم تقريبا إلى الزاوية الشمالية الغربية من أراضي خربة أخزاعة ومن هناك تتبع خط حدود هذه القرية إلى أقصى نقطة جنوبية منها. بعد ذلك تسير في اتجاه جنوبي على محاذاة خط الطول 90 حتى نقطة تقاطعه مع خط العرض 70 ثم تنعطف في اتجاه جنوبي شرقي إلى خربة الرحيبة وتمضي في اتجاه جنوبي إلى نقطة معروفة باسم البها، حيث تعبر من خلفها طريق بئر السبع/ العوجا العام إلى الغرب من خربة المشرف، ومن هناك تلتقي بوادي الزياتين إلى الغرب من السبيطة ومن هناك تنعطف إلى الشمال الشرقي ثم إلى الجنوب الشرقي تابعة هذا الوادي ثم تمضي إلى الشرق من عبدة فتلتقي بوادي النفخ. وتبرز بعد ذلك إلى الجنوب الغربي على محاذاة وادي النفخ ووادي عجرم ووداي لسان حتى النقطة التي تقطع فيها وادي لسان الحدود المصرية.
تتكون منطقة قطاع يافا العربي من ذلك الجزء من منطقة تخطيط مدينة يافا التي تقع إلى الغرب من الأحياء اليهودية الواقعة جنوبي تل أبيب، وإلى الغرب من امتداد شارع هرتزل حتى التقائه بطريق يافا/ القدس، وإلى الجنوب الغربي من ذلك الجزء من طريق يافا/ القدس الواقع إلى الجنوب الشرقي من نقطة الالتقاء تلك، وإلى الغرب من أراضي مكفيه يسرائيل وإلى الشمال الغربي من منطقة مجلس حولون المحلي، وإلى الشمال من الخط الذي يصل الزاوية الشمالية الغربية من حولون بالزاوية الشمالية الشرقية من منطقة مجلس بات يام المحلي، وإلى الشمال من منطقة مجلس بات يام المحلي. أما مسألة حي الكاترون فستبتها لجنة الحدود بحيث تأخذ بعين الاعتبار -إضافة إلى الاعتبارات الأخرى- الرغبة في ضم أقل عدد ممكن من سكانه العرب وأكبر عدد ممكن من سكانه اليهود إلى الدولة اليهودية.
ب- الدولة اليهودية
تحد القطاع الشمالي الشرقي من الدولة اليهودية (الجليل الشرقي) من الشمال والغرب والحدود اللبنانية، ومن الشرق حدود سوريا وشرق الأردن. ويضم كل حوض الحولة وبحيرة طبريا وكل مقاطعة بيسان، حيث يمتد خط الحدود إلى قمة جبال الجلبوع ووداي المالح. ومن هناك تمتد الدولة اليهودية نحو الشمال الغربي ضمن الحدود التي وصفت فيما يتعلق بالدولة العربية.
يمتد الجزء اليهودي من السهل الساحلي من نقطة بين ميناء القلاع والنبي يونس في مقاطعة غزة، ويضم مدينتي حيفا وتل أبيب تاركا يافا قطاعا تابعا للدولة العربية. وتتبع الحدود الشرقية للدولة اليهودية الحدود التي وصفت فيما يتصل بالدولة العربية.
ج- مدينة القدس
تكون حدود مدينة القدس كما هي محددة في التوصيات المتعلقة بمدينة القدس. (راجع أدناه الجزء الثالث، القسم ب).
الجزء الثالث: مدينة القدس
أ- نظام خاص
يجعل لمدينة القدس كيان منفصل (Corpus Sepratum) خاضع لنظام دولي خاص، وتتولى الأمم المتحدة إدارتها، ويعين مجلس وصاية ليقوم بأعمال السلطة الإدارية نيابة عن الأمم المتحدة.
ب- حدود المدينة
تشمل مدينة القدس بلدية القدس الحالية مضافا إليها القرى والبلدان المجاورة، وأبعدها شرقا أبو ديس، وأبعدها جنوبا بيت لحم، وغربا عين كارم. وتشمل معها المنطقة المبنية من قرية قالونيا.
ج- نظام المدينة الأساسي
على مجلس الوصاية خلال خمسة أشهر من الموافقة على المشروع الحاضر، أن يضع ويقر دستورا مفصلا للمدينة يتضمن جوهر الشروط التالية:
الإدارة الحكومية، مقاصدها الخاصة:
على السلطة الإدارية أن تتبع في أثناء قيامها بالتزاماتها الإدارية الأهداف الخاصة التالية:
أ- حماية المصالح الروحية والدينية الفريدة الواقعة ضمن مدينة العقائد التوحيدية الكبيرة الثلاث المنتشرة في أنحاء العالم -المسيحية واليهودية والإسلام- وصيانتها، والعمل لهذه الغاية بحيث يسود النظام والسلام -السلام الديني خاصة- مدينة القدس.
ب- دعم روح التعاون بين سكان المدينة جميعهم، سواء في سبيل مصلحتهم الخاصة أم في سبيل تشجيع التطور السلمي للعلاقات المشتركة بين شعبي فلسطين في البلاد المقدسة بأسرها، وتأمين الأمن والرفاهية، وتشجيع كل تدبير بناء من شأنه أن يحسن حياة السكان، آخذا بعين الاعتبار العادات والظروف الخاصة لمختلف الشعوب والجاليات.
الحاكم والموظفون الإداريون:
يقوم مجلس الوصاية بتعيين حاكم للقدس يكون مسؤولا أمامه، ويكون هذا الاختيار على أساس كفايته الخاصة دون مراعاة لجنسيته، على ألا يكون مواطنا لأي من الدولتين في فلسطين.
مثل الحاكم الأمم المتحدة في مدينة القدس، ويمارس نيابة عنها جميع السلطات الإدارية بما في ذلك إدارة الشؤون الخارجية، وتعاونه مجموعة من الموظفين الإداريين يعتبر أفرادها موظفين دوليين وفق منطوق المادة (100) من الميثاق، ويختارون قدر الإمكان من بين سكان المدينة ومن سائر فلسطين دون أي تمييز عنصري. وعلى الحاكم أن يقدم مشروعا مفصلا لتنظيم إدارة المدينة إلى مجلس الوصاية لينال موافقته عليه.
الاستقلال المحلي:
أ- يكون للوحدات القائمة حاليا ذات الاستقلال المحلي في منطقة المدينة (القرى والمراكز والبلديات) سلطات حكومية وإدارية واسعة ضمن النطاق المحلي.
ب- يدرس الحاكم مشروع إنشاء وحدات بلدية خاصة تتألف من الأقسام اليهودية والعربية في مدينة القدس الجديدة، ويرفعه إلى مجلس الوصاية للنظر فيه وإصدار قرار بشأنه. وتستمر الوحدات البلدية الجديدة في تكوين جزء من البلدية الحالية لمدينة القدس.
تدابير الأمن:
أ- تجرد مدينة القدس من السلاح ويعلن حيادها ويحافظ عليه، ولا يسمح بقيام أية تشكيلات أو تدريب أو نشاط عسكري ضمن حدودها.
ب- في حال عرقلة أعمال الإدارة في مدينة القدس بصورة خطيرة أو منعها من جراء عدم تعاون أو تدخل فئة أو أكثر من السكان، يكون للحاكم السلطة باتخاذ التدابير اللازمة لإعادة سير الإدارة الفعال.
ج- للمساعدة على استتباب القانون والنظام الداخلي، وبصورة خاصة لحماية الأماكن المقدسة والمواقع والأبنية الدينية في المدينة، يقوم الحاكم بتنظيم شرطة خاصة ذات قوة كافية يجد أفرادها من خارج فلسطين ويعطى الحاكم الحق في التصرف في بنود الميزانية بحسب الحاجة للمحافظة على هذه القوة والاتفاق عليها.
التنظيم التشريعي:
تكون السلطة التشريعية والضرائبية بيد مجلس تشريعي منتخب بالاقتراع العام السري، على أساس تمثيل نسبي لسكان مدينة القدس البالغين، وبغير تمييز من حيث الجنسية. ومع ذلك يجب ألا يتعارض أي إجراء تشريعي أو يتناقض مع الأحكام المنصوص عليها في دستور المدينة، كما يجب ألا يسود هذه الأحكام أي قانون أو لائحة أو تصرف رسمي ويعطي الدستور الحاكم الحق في الاعتراض (VETO) على مشاريع القوانين المتنافية مع الأحكام المذكورة، ويمنحه كذلك سلطة إصدار أوامر وقتية في حال تخلف المجلس عن الموافقة في الوقت الملائم على مشروع قانون يعتبر جوهريا بالنسبة إلى سير الإدارة الطبيعي.
القضاء:
يجب أن ينص القانون على إنشاء نظام قضائي مستقل، يشتمل على محكمة استئناف يخضع لولايتها سكان المدينة.
الاتحاد الاقتصادي والنظام الاقتصادي:
تكون مدينة القدس داخلة ضمن الاتحاد الاقتصادي الفلسطيني ومقيدة بأحكام التعهد جميعها وبكل معاهدة تنبثق منه، وكذلك بجميع قرارات المجلس الاقتصادي المشترك. ويقام مقر المجلس الاقتصادي في منطقة المدينة ويجب أن يحتوي الدستور على أحكام للشؤون الاقتصادية التي لا تقع ضمن نظام الوحدة الاقتصادية، وذلك على أساس من عدم التمييز والمساواة في المعاملة بالنسبة إلى الدول الأعضاء في الأمم المتحدة ورعاياها.
حرية العبور TRANSIT والزيارة والسيطرة على المقيمين:
تكون حرية الدخول والإقامة ضمن حدود المدينة مضمونة للمقيمين في الدولتين العربية واليهودية ولمواطنيها وذلك بشرط عدم الإخلال باعتبارات الأمن، مع مراعاة الاعتبارات الاقتصادية كما يحددها الحاكم وفقا لتعليمات مجلس الوصاية. وتكون الهجرة إلى داخل حدود المدينة والإقامة فيها بالنسبة إلى رعايا الدول الأخرى، خاضعة لسلطة الحاكم وفقا لتعليمات مجلس الوصاية.
العلاقات بالدولتين العربية واليهودية:
يعتمد الحاكم للمدينة ممثلي الدولتين العربية واليهودية، ويكونان مكلفين بحماية مصالح دولتيهما ورعاياهما لدى الإدارة الدولية للمدينة.
اللغات الرسمية:
تكون العربية والعبرية لغتي المدينة الرسميتين، ولا يحول هذا النص دون أن يعتمد في العمل لغة أو لغات إضافية عدة بحسب الحاجة.
المواطنة:
يصبح جميع المقيمين بحكم الواقع مواطنين في مدينة القدس، ما لم يختاروا جنسية الدولة التي كانوا رعاياها، أو ما لم يكونوا عربا أو يهودا قد أعلنوا نيتهم أن يصبحوا مواطنين في الدولة العربية والدولة اليهودية طبقا للفقرة (9) من القسم (ب) من الجزء الأول من المشروع الحاضر.
ويتخذ مجلس الوصاية التدابير لتوفير الحماية القنصلية لمواطني المدينة خارج أرضها.
حريات المواطنين:
أ- يضمن لسكان المدينة -بشرط عدم الإخلال بمقتضيات النظام العام والآداب العامة- حقوق الإنسان والحريات الأساسية، مشتملة حرية العقيدة والدين والعبادة واللغة والتعليم وحرية القول وحرية الصحافة وحرية الاجتماع والانتماء إلى الجمعيات وتكوينها، وحرية التظلم.
ب- لا يجري أي تمييز بين السكان بسبب الأصل أو الدين أو اللغة أو الجنس.
ج- يكون لجميع المقيمين داخل المدينة حق متساو في التمتع بحماية القانون.
د- يجب احترام قانون الأسرة والأحوال الشخصية لمختلف الأفراد ومختلف الطوائف، كما تحترم كذلك مصالحهم الدينية.
هـ- مع عدم الإخلال بضرورات النظام العام وحسن الإدارة لا يتخذ أي إجراء يعوق أو يتدخل في نشاط المؤسسات الدينية أو الخيرية لجميع المذاهب، ولا يجوز عمل أي تمييز نحو ممثلي هذه المؤسسات أو أعضائها بسبب دينهم أو جنسيتهم.
و- تؤمن المدينة تعليما ابتدائيا وثانويا كافيين للطائفتين العربية واليهودية كل بلغتها ووفق تقاليدها الثقافية. وإن حقوق كل طائفة في الاحتفاظ بمدارسها الخاصة لتعليم أفرادها بلغتهم القومية -شرط أن تلتزم بمتطلبات التعليم العامة التي قد تفرضها المدينة- لن تنكر أو تعطل. أما مؤسسات التعليم الأجنبية فتتابع نشاطها على أساس الحقوق القائمة.
ز- لا يجوز أن تحد حرية أي فرد من سكان المدينة في استخدام أية لغة كانت في أحاديثه الخاصة، أو في التجارة أو الأمور الدينية، أو الصحافة أو المنشورات بجميع أنواعها، أو الاجتماعات العامة.
الأماكن المقدسة:
أ- لا يجوز أن يلحق أي مساس بالحقوق القائمة الحالية المتعلقة بالأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية.
ب- تضمن حرية الوصول إلى الأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية، وحرية ممارسة العبادة، وفقا للحقوق القائمة شرط مراعاة حفظ النظام واللياقة.
ج- تصان الأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية ويحرم كل فعل من شأنه أن يسيء بأية صورة كانت إلى قداستها. وإن رأى الحاكم في أي وقت ضرورة ترميم مكان مقدس أو بناء موقع ديني ما، فيجوز له أن يدعو الطائفة أو الطوائف المعنية إلى القيام بالترميمات اللازمة. ويجوز له القيام بهذه الترميمات على حساب الطائفة أو الطوائف المعنية إن لم يتلق جوابا عن طلبه خلال مدة معقولة.
د- لا تجبى أية ضريبة على مكان مقدس أو مبنى أو موقع ديني كان معفيا منها وقت إقامة المدينة (بوضعها الدولي)، ولا يلحق أي تعديل في هذه الضريبة يكون من شأنه التمييز بين مالكي الأماكن والأبنية والمواقع الدينية أو ساكنيها، أو يكون من شأنه وضع هؤلاء المالكين أو الساكنين من أثر الضريبة العام في وضع أقل ملاءمة مما كان عليه حالهم وقت تبني توصيات الجمعية العامة.
سلطات الحاكم الخاصة فيما يتعلق بالأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية في المدينة وفي أي جزء من فلسطين:
أ- إن حماية الأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية الموجودة في مدينة القدس، يجب أن تكون موضع اهتمام الحاكم بصورة خاصة.
ب- وفيما يتعلق بالأماكن والأبنية والمواقع المماثلة الموجودة في فلسطين خارج المدينة يقر الحاكم -بموجب السلطات التي يكون قد منحه إياها دستور الدولتين- ما إذا كانت أحكام دستوري الدولتين العربية واليهودية في فلسطين والخاصة بهذه الأماكن وبالحقوق الدينية المتعلقة بها، مطبقة ومحترمة كما يجب.
ج- وللحاكم كذلك الحق في اتخاذ القرارات على أساس الحقوق القائمة في حال حدوث خلاف بين مختلف الطوائف الدينية أو بشأن شعائر طائفة ما بالنسبة إلى الأماكن المقدسة والأبنية والمواقع الدينية في سائر أنحاء فلسطين.
ويجوز للحاكم أن يستعين في أثناء قيامه بهذه المهمة بمجلس استشاري مؤلف من ممثلين لمختلف الطوائف يعملون بصفة استشارية.
د- مدة نظام الحكم الخاص
يبدأ تنفيذ الدستور الذي يضعه مجلس الوصاية -في ضوء المبادئ المذكورة أعلاه- في ميعاد أقصاه أول أكتوبر/ تشرين الأول 1948، ويكون سريانه أول الأمر خلال عشر سنوات ما لم ير مجلس الوصاية وجوب القيام في أقرب وقت بإعادة النظر في هذه الأحكام. ويجب عند انقضاء هذه المدة أن يعاد النظر في مجموع النظام من قبل مجلس الوصاية في ضوء التجارب المكتسبة خلال هذه الفترة من العمل به. وعندئذ يكون للمقيمين في المدينة الحرية في الإعلان، بطريق الاستفتاء، عن رغباتهم في التعديلات الممكن إجراؤها على نظام المدينة.
الجزء الرابع: الامتيازات
إن الدول التي يكون رعاياها قد تمتعوا في الماضي في فلسطين بالمزايا والحصانات القنصلية التي كانت ممنوحة لهم في أثناء الحكم العثماني بموجب الامتيازات أو العرف، مدعوة إلى التنازل عن جميع حقوقها في إعادة تثبيت المزايا والحصانات المذكورة في الدولتين العربية واليهودية المنوي إنشاؤهما وكذلك في مدينة القدس.
تبنت الجمعية العامة هذا القرار في جلستها العامة رقم 128 بـ23 صوتا مقابل 13 وامتناع 10 كالآتي:
مع القرار: أستراليا، بلجيكا، بوليفيا، البرازيل، بيلاروسيا (روسيا البيضاء)، كندا، كوستاريكا، تشيكوسلوفاكيا، الدانمارك، جمهورية الدومينيكان، إكوادور، فرنسا، غواتيمالا، هاييتي، إيسلندا، ليبيريا، لوكسمبورغ، هولندا، نيوزيلندا، نيكاراغوا، النرويج، بنما، باراغواي، بيرو، الفلبين، بولندا، السويد، أوكرانيا، جنوب أفريقيا، الاتحاد السوفياتي، الولايات المتحدة الأميركية، أوروغواي، فنزويلا.
ضد القرار: أفغانستان، كوبا، مصر، اليونان، الهند، إيران، العراق، لبنان، باكستان، المملكة العربية السعودية، سوريا، تركيا، اليمن.
امتناع: الأرجنتين، الشيلي، الصين، كولومبيا، السلفادور، الحبشة، هندوراس، المكسيك، المملكة المتحدة، يوغسلافيا.
_______________
المصدر
قرارات الأمم المتحدة بشأن فلسطين والصراع العربي الإسرائيلي، المجلد الأول، 1947 - 1974، مؤسسة الدراسات الفلسطينية، نقلا عن المحاضر الرسمية للجمعية العامة، الدورة 2، الملحق رقم 11، المجلد الأول إلى الرابع.
نص القرار باللغة الانجليزية
A
General Assembly
A/RES/181(II)
29 November 1947
Resolution 181 (II). Future government of Palestine
A
The General Assembly,
Having met in special session at the request of the mandatory Power to constitute and instruct a special committee to prepare for the consideration of the question of the future government of Palestine at the second regular session;
Having constituted a Special Committee and instructed it to investigate all questions and issues relevant to the problem of Palestine, and to prepare proposals for the solution of the problem, and
Having received and examined the report of the Special Committee (document A/364) 1/ including a number of unanimous recommendations and a plan of partition with economic union approved by the majority of the Special Committee,
Considers that the present situation in Palestine is one which is likely to impair the general welfare and friendly relations among nations;
Takes note of the declaration by the mandatory Power that it plans to complete its evacuation of Palestine by 1 August 1948;
Recommends to the United Kingdom, as the mandatory Power for Palestine, and to all other Members of the United Nations the adoption and implementation, with regard to the future government of Palestine, of the Plan of Partition with Economic Union set out below;
Requests that
(a) The Security Council take the necessary measures as provided for in the plan for its implementation;
(b) The Security Council consider, if circumstances during the transitional period require such consideration, whether the situation in Palestine constitutes a threat to the peace. If it decides that such a threat exists, and in order to maintain international peace and security, the Security Council should supplement the authorization of the General Assembly by taking measures, under Articles 39 and 41 of the Charter, to empower the United Nations Commission, as provided in this resolution, to exercise in Palestine the functions which are assigned to it by this resolution;
(c) The Security Council determine as a threat to the peace, breach of the peace or act of aggression, in accordance with Article 39 of the Charter, any attempt to alter by force the settlement envisaged by this resolution;
(d) The Trusteeship Council be informed of the responsibilities envisaged for it in this plan;
Calls upon the inhabitants of Palestine to take such steps as may be necessary on their part to put this plan into effect;
Appeals to all Governments and all peoples to refrain from taking action which might hamper or delay the carrying out of these recommendations, and
Authorizes the Secretary-General to reimburse travel and subsistence expenses of the members of the Commission referred to in Part I, Section B, paragraph 1 below, on such basis and in such form as he may determine most appropriate in the circumstances, and to provide the Commission with the necessary staff to assist in carrying out the functions assigned to the Commission by the General Assembly.
B 2/
The General Assembly
Authorizes the Secretary-General to draw from the Working Capital Fund a sum not to exceed $2,000,000 for the purposes set forth in the last paragraph of the resolution on the future government of Palestine.
Hundred and twenty-eighth plenary meeting
29 November 1947
[At its hundred and twenty-eighth plenary meeting on 29 November 1947 the General Assembly, in accordance with the terms of the above resolution [181 A], elected the following members of the United Nations Commission on Palestine: Bolivia, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, Panama and Philippines.]
PLAN OF PARTITION WITH ECONOMIC UNION
PART I
Future constitution and government of Palestine
A. TERMINATION OF MANDATE, PARTITION AND INDEPENDENCE
1. The Mandate for Palestine shall terminate as soon as possible but in any case not later than 1 August 1948.
2. The armed forces of the mandatory Power shall be progressively withdrawn from Palestine, the withdrawal to be completed as soon as possible but in any case not later than 1 August 1948.
The mandatory Power shall advise the Commission, as far in advance as possible, of its intention to terminate the Mandate and to evacuate each area.
The mandatory Power shall use its best endeavours to ensure than an area situated in the territory of the Jewish State, including a seaport and hinterland adequate to provide facilities for a substantial immigration, shall be evacuated at the earliest possible date and in any event not later than 1 February 1948.
3. Independent Arab and Jewish States and the Special International Regime for the City of Jerusalem, set forth in part III of this plan, shall come into existence in Palestine two months after the evacuation of the armed forces of the mandatory Power has been completed but in any case not later than 1 October 1948. The boundaries of the Arab State, the Jewish State, and the City of Jerusalem shall be as described in parts II and III below.
4. The period between the adoption by the General Assembly of its recommendation on the question of Palestine and the establishment of the independence of the Arab and Jewish States shall be a transitional period.
B. STEPS PREPARATORY TO INDEPENDENCE
1. A Commission shall be set up consisting of one representative of each of five Member States. The Members represented on the Commission shall be elected by the General Assembly on as broad a basis, geographically and otherwise, as possible.
2. The administration of Palestine shall, as the mandatory Power withdraws its armed forces, be progressively turned over to the Commission; which shall act in conformity with the recommendations of the General Assembly, under the guidance of the Security Council. The mandatory Power shall to the fullest possible extent co-ordinate its plans for withdrawal with the plans of the Commission to take over and administer areas which have been evacuated.
In the discharge of this administrative responsibility the Commission shall have authority to issue necessary regulations and take other measures as required.
The mandatory Power shall not take any action to prevent, obstruct or delay the implementation by the Commission of the measures recommended by the General Assembly.
3. On its arrival in Palestine the Commission shall proceed to carry out measures for the establishment of the frontiers of the Arab and Jewish States and the City of Jerusalem in accordance with the general lines of the recommendations of the General Assembly on the partition of Palestine. Nevertheless, the boundaries as described in part II of this plan are to be modified in such a way that village areas as a rule will not be divided by state boundaries unless pressing reasons make that necessary.
4. The Commission, after consultation with the democratic parties and other public organizations of The Arab and Jewish States, shall select and establish in each State as rapidly as possible a Provisional Council of Government. The activities of both the Arab and Jewish Provisional Councils of Government shall be carried out under the general direction of the Commission.
If by 1 April 1948 a Provisional Council of Government cannot be selected for either of the States, or, if selected, cannot carry out its functions, the Commission shall communicate that fact to the Security Council for such action with respect to that State as the Security Council may deem proper, and to the Secretary-General for communication to the Members of the United Nations.
5. Subject to the provisions of these recommendations, during the transitional period the Provisional Councils of Government, acting under the Commission, shall have full authority in the areas under their control, including authority over matters of immigration and land regulation.
6. The Provisional Council of Government of each State acting under the Commission, shall progressively receive from the Commission full responsibility for the administration of that State in the period between the termination of the Mandate and the establishment of the State's independence.
7. The Commission shall instruct the Provisional Councils of Government of both the Arab and Jewish States, after their formation, to proceed to the establishment of administrative organs of government, central and local.
8. The Provisional Council of Government of each State shall, within the shortest time possible, recruit an armed militia from the residents of that State, sufficient in number to maintain internal order and to prevent frontier clashes.
This armed militia in each State shall, for operational purposes, be under the command of Jewish or Arab officers resident in that State, but general political and military control, including the choice of the militia's High Command, shall be exercised by the Commission.
9. The Provisional Council of Government of each State shall, not later than two months after the withdrawal of the armed forces of the mandatory Power, hold elections to the Constituent Assembly which shall be conducted on democratic lines.
The election regulations in each State shall be drawn up by the Provisional Council of Government and approved by the Commission. Qualified voters for each State for this election shall be persons over eighteen years of age who are: (a) Palestinian citizens residing in that State and (b) Arabs and Jews residing in the State, although not Palestinian citizens, who, before voting, have signed a notice of intention to become citizens of such State.
Arabs and Jews residing in the City of Jerusalem who have signed a notice of intention to become citizens, the Arabs of the Arab State and the Jews of the Jewish State, shall be entitled to vote in the Arab and Jewish States respectively.
Women may vote and be elected to the Constituent Assemblies.
During the transitional period no Jew shall be permitted to establish residence in the area of the proposed Arab State, and no Arab shall be permitted to establish residence in the area of the proposed Jewish State, except by special leave of the Commission.
10. The Constituent Assembly of each State shall draft a democratic constitution for its State and choose a provisional government to succeed the Provisional Council of Government appointed by the Commission. The constitutions of the States shall embody chapters 1 and 2 of the Declaration provided for in section C below and include inter alia provisions for:
(a) Establishing in each State a legislative body elected by universal suffrage and by secret ballot on the basis of proportional representation, and an executive body responsible to the legislature;
(b) Settling all international disputes in which the State may be involved by peaceful means in such a manner that international peace and security, and justice, are not endangered;
(c) Accepting the obligation of the State to refrain in its international relations from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity of political independence of any State, or in any other manner inconsistent with the purposes of the United Nations;
(d) Guaranteeing to all persons equal and non-discriminatory rights in civil, political, economic and religious matters and the enjoyment of human rights and fundamental freedoms, including freedom of religion, language, speech and publication, education, assembly and association;
(e) Preserving freedom of transit and visit for all residents and citizens of the other State in Palestine and the City of Jerusalem, subject to considerations of national security, provided that each State shall control residence within its borders.
11. The Commission shall appoint a preparatory economic commission of three members to make whatever arrangements are possible for economic co-operation, with a view to establishing, as soon as practicable, the Economic Union and the Joint Economic Board, as provided in section D below.
12. During the period between the adoption of the recommendations on the question of Palestine by the General Assembly and the termination of the Mandate, the mandatory Power in Palestine shall maintain full responsibility for administration in areas from which it has not withdrawn its armed forces. The Commission shall assist the mandatory Power in the carrying out of these functions. Similarly the mandatory Power shall co-operate with the Commission in the execution of its functions.
13. With a view to ensuring that there shall be continuity in the functioning of administrative services and that, on the withdrawal of the armed forces of the mandatory Power, the whole administration shall be in the charge of the Provisional Councils and the Joint Economic Board, respectively, acting under the Commission, there shall be a progressive transfer, from the mandatory Power to the Commission, of responsibility for all the functions of government, including that of maintaining law and order in the areas from which the forces of the mandatory Power have been withdrawn.
14. The Commission shall be guided in its activities by the recommendations of the General Assembly and by such instructions as the Security Council may consider necessary to issue.
The measures taken by the Commission, within the recommendations of the General Assembly, shall become immediately effective unless the Commission has previously received contrary instructions from the Security Council.
The Commission shall render periodic monthly progress reports, or more frequently if desirable, to the Security Council.
15. The Commission shall make its final report to the next regular session of the General Assembly and to the Security Council simultaneously.
C. DECLARATION
A declaration shall be made to the United Nations by the provisional government of each proposed State before independence. It shall contain inter alia the following clauses:
General Provision
The stipulations contained in the declaration are recognized as fundamental laws of the State and no law, regulation or official action shall conflict or interfere with these stipulations, nor shall any law, regulation or official action prevail over them.
Chapter 1
Holy Places, religious buildings and sites
1. Existing rights in respect of Holy Places and religious buildings or sites shall not be denied or impaired.
2. In so far as Holy Places are concerned, the liberty of access, visit and transit shall be guaranteed, in conformity with existing rights, to all residents and citizens of the other State and of the City of Jerusalem, as well as to aliens, without distinction as to nationality, subject to requirements of national security, public order and decorum.
Similarly, freedom of worship shall be guaranteed in conformity with existing rights, subject to the maintenance of public order and decorum.
3. Holy Places and religious buildings or sites shall be preserved. No act shall be permitted which may in any way impair their sacred character. If at any time it appears to the Government that any particular Holy Place, religious building or site is in need of urgent repair, the Government may call upon the community or communities concerned to carry out such repair. The Government may carry it out itself at the expense of the community or communities concerned if no action is taken within a reasonable time.
4. No taxation shall be levied in respect of any Holy Place, religious building or site which was exempt from taxation on the date of the creation of the State.
No change in the incidence of such taxation shall be made which would either discriminate between the owners or occupiers of Holy Places, religious buildings or sites, or would place such owners or occupiers in a position less favourable in relation to the general incidence of taxation than existed at the time of the adoption of the Assembly's recommendations.
5. The Governor of the City of Jerusalem shall have the right to determine whether the provisions of the Constitution of the State in relation to Holy Places, religious buildings and sites within the borders of the State and the religious rights appertaining thereto, are being properly applied and respected, and to make decisions on the basis of existing rights in cases of disputes which may arise between the different religious communities or the rites of a religious community with respect to such places, buildings and sites. He shall receive full co-operation and such privileges and immunities as are necessary for the exercise of his functions in the State.
Chapter 2
Religious and Minority Rights
1. Freedom of conscience and the free exercise of all forms of worship, subject only to the maintenance of public order and morals, shall be ensured to all.
2. No discrimination of any kind shall be made between the inhabitants on the ground of race, religion, language or sex.
3. All persons within the jurisdiction of the State shall be entitled to equal protection of the laws.
4. The family law and personal status of the various minorities and their religious interests, including endowments, shall be respected.
5. Except as may be required for the maintenance of public order and good government, no measure shall be taken to obstruct or interfere with the enterprise of religious or charitable bodies of all faiths or to discriminate against any representative or member of these bodies on the ground of his religion or nationality.
6. The State shall ensure adequate primary and secondary education for the Arab and Jewish minority, respectively, in its own language and its cultural traditions.
The right of each community to maintain its own schools for the education of its own members in its own language, while conforming to such educational requirements of a general nature as the State may impose, shall not be denied or impaired. Foreign educational establishments shall continue their activity on the basis of their existing rights.
7. No restriction shall be imposed on the free use by any citizen of the State of any language in private intercourse, in commerce, in religion, in the Press or in publications of any kind, or at public meetings.3/
8. No expropriation of land owned by an Arab in the Jewish State (by a Jew in the Arab State)4/ shall be allowed except for public purposes. In all cases of expropriation full compensation as fixed by the Supreme Court shall be paid previous to dispossession.
Chapter 3
Citizenship, international conventions and financial obligations
1. Citizenship. Palestinian citizens residing in Palestine outside the City of Jerusalem, as well as Arabs and Jews who, not holding Palestinian citizenship, reside in Palestine outside the City of Jerusalem shall, upon the recognition of independence, become citizens of the State in which they are resident and enjoy full civil and political rights. Persons over the age of eighteen years may opt, within one year from the date of recognition of independence of the State in which they reside, for citizenship of the other State, providing that no Arab residing in the area of the proposed Arab State shall have the right to opt for citizenship in the proposed Jewish State and no Jew residing in the proposed Jewish State shall have the right to opt for citizenship in the proposed Arab State. The exercise of this right of option will be taken to include the wives and children under eighteen years of age of persons so opting.
Arabs residing in the area of the proposed Jewish State and Jews residing in the area of the proposed Arab State who have signed a notice of intention to opt for citizenship of the other State shall be eligible to vote in the elections to the Constituent Assembly of that State, but not in the elections to the Constituent Assembly of the State in which they reside.
2. International conventions. (a) The State shall be bound by all the international agreements and conventions, both general and special, to which Palestine has become a party. Subject to any right of denunciation provided for therein, such agreements and conventions shall be respected by the State throughout the period for which they were concluded.
(b) Any dispute about the applicability and continued validity of international conventions or treaties signed or adhered to by the mandatory Power on behalf of Palestine shall be referred to the International Court of Justice in accordance with the provisions of the Statute of the Court.
3. Financial obligations. (a) The State shall respect and fulfil all financial obligations of whatever nature assumed on behalf of Palestine by the mandatory Power during the exercise of the Mandate and recognized by the State. This provision includes the right of public servants to pensions, compensation or gratuities.
(b) These obligations shall be fulfilled through participation in the Joint economic Board in respect of those obligations applicable to Palestine as a whole, and individually in respect of those applicable to, and fairly apportionable between, the States.
(c) A Court of Claims, affiliated with the Joint Economic Board, and composed of one member appointed by the United Nations, one representative of the United Kingdom and one representative of the State concerned, should be established. Any dispute between the United Kingdom and the State respecting claims not recognized by the latter should be referred to that Court.
(d) Commercial concessions granted in respect of any part of Palestine prior to the adoption of the resolution by the General Assembly shall continue to be valid according to their terms, unless modified by agreement between the concession-holder and the State.
Chapter 4
Miscellaneous provisions
1. The provisions of chapters 1 and 2 of the declaration shall be under the guarantee of the United Nations, and no modifications shall be made in them without the assent of the General Assembly of the United nations. Any Member of the United Nations shall have the right to bring to the attention of the General Assembly any infraction or danger of infraction of any of these stipulations, and the General Assembly may thereupon make such recommendations as it may deem proper in the circumstances.
2. Any dispute relating to the application or the interpretation of this declaration shall be referred, at the request of either party, to the International Court of Justice, unless the parties agree to another mode of settlement.
D. ECONOMIC UNION AND TRANSIT
1. The Provisional Council of Government of each State shall enter into an undertaking with respect to economic union and transit. This undertaking shall be drafted by the commission provided for in section B, paragraph 1, utilizing to the greatest possible extent the advice and co-operation of representative organizations and bodies from each of the proposed States. It shall contain provisions to establish the Economic Union of Palestine and provide for other matters of common interest. If by 1 April 1948 the Provisional Councils of Government have not entered into the undertaking, the undertaking shall be put into force by the Commission.
The Economic Union of Palestine
2. The objectives of the Economic Union of Palestine shall be:
(a) A customs union;
(b) A joint currency system providing for a single foreign exchange rate;
(c) Operation in the common interest on a non-discriminatory basis of railways; inter-State highways; postal, telephone and telegraphic services, and port and airports involved in international trade and commerce;
(d) Joint economic development, especially in respect of irrigation, land reclamation and soil conservation;
(e) Access for both States and for the City of Jerusalem on a non-discriminatory basis to water and power facilities.
3. There shall be established a Joint Economic Board, which shall consist of three representatives of each of the two States and three foreign members appointed by the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations. The foreign members shall be appointed in the first instance for a term of three years; they shall serve as individuals and not as representatives of States.
4. The functions of the Joint Economic Board shall be to implement either directly or by delegation the measures necessary to realize the objectives of the Economic Union. It shall have all powers of organization and administration necessary to fulfil its functions.
5. The States shall bind themselves to put into effect the decisions of the Joint Economic Board. The Board's decisions shall be taken by a majority vote.
6. In the event of failure of a State to take the necessary action the Board may, by a vote of six members, decide to withhold an appropriate portion of that part of the customs revenue to which the State in question is entitled under the Economic Union. Should the State persist in its failure to co-operate, the Board may decide by a simple majority vote upon such further sanctions, including disposition of funds which it has withheld, as it may deem appropriate.
7. In relation to economic development, the functions of the Board shall be the planning, investigation and encouragement of joint development projects, but it shall not undertake such projects except with the assent of both States and the City of Jerusalem, in the event that Jerusalem is directly involved in the development project.
8. In regard to the joint currency system the currencies circulating in the two States and the City of Jerusalem shall be issued under the authority of the Joint Economic Board, which shall be the sole issuing authority and which shall determine the reserves to be held against such currencies.
9. So far as is consistent with paragraph 2 (b) above, each State may operate its own central bank, control its own fiscal and credit policy, its foreign exchange receipts and expenditures, the grant of import licenses, and may conduct international financial operations on its own faith and credit. During the first two years after the termination of the Mandate, the Joint Economic Board shall have the authority to take such measures as may be necessary to ensure that--to the extent that the total foreign exchange revenues of the two States from the export of goods and services permit, and provided that each State takes appropriate measures to conserve its own foreign exchange resources--each State shall have available, in any twelve months' period, foreign exchange sufficient to assure the supply of quantities of imported goods and services for consumption in its territory equivalent to the quantities of such goods and services consumed in that territory in the twelve months' period ending 31 December 1947.
10. All economic authority not specifically vested in the Joint Economic Board is reserved to each State.
11. There shall be a common customs tariff with complete freedom of trade between the States, and between the States and the City of Jerusalem.
12. The tariff schedules shall be drawn up by a Tariff Commission, consisting of representatives of each of the States in equal numbers, and shall be submitted to the Joint Economic Board for approval by a majority vote. In case of disagreement in the Tariff Commission, the Joint Economic Board shall arbitrate the points of difference. In the event that the Tariff Commission fails to draw up any schedule by a date to be fixed, the Joint Economic Board shall determine the tariff schedule.
13. The following items shall be a first charge on the customs and other common revenue of the Joint Economic Board:
(a) The expenses of the customs service and of the operation of the joint services;
(b) The administrative expenses of the Joint Economic Board;
(c) The financial obligations of the Administration of Palestine consisting of:
(i) The service of the outstanding public debt;
(ii) The cost of superannuation benefits, now being paid or falling due in the future, in accordance with the rules and to the extent established by paragraph 3 of chapter 3 above.
14. After these obligations have been met in full, the surplus revenue from the customs and other common services shall be divided in the following manner: not less than 5 per cent and not more than 10 per cent to the City of Jerusalem; the residue shall be allocated to each State by the Joint Economic Board equitably, with the objective of maintaining a sufficient and suitable level of government and social services in each State, except that the share of either State shall not exceed the amount of that State's contribution to the revenues of the Economic Union by more than approximately four million pounds in any year. The amount granted may be adjusted by the Board according to the price level in relation to the prices prevailing at the time of the establishment of the Union. After five years, the principles of the distribution of the joint revenues may be revised by the Joint Economic Board on a basis of equity.
15. All international conventions and treaties affecting customs tariff rates, and those communications services under the jurisdiction of the Joint Economic Board, shall be entered into by both States. In these matters, the two States shall be bound to act in accordance with the majority vote of the Joint Economic Board.
16. The Joint Economic Board shall endeavour to secure for Palestine's export fair and equal access to world markets.
17. All enterprises operated by the Joint Economic Board shall pay fair wages on a uniform basis.
Freedom of transit and visit
18. The undertaking shall contain provisions preserving freedom of transit and visit for all residents or citizens of both States and of the City of Jerusalem, subject to security considerations; provided that each state and the City shall control residence within its borders.
Termination, modification and interpretation of the undertaking
19. The undertaking and any treaty issuing therefrom shall remain in force for a period of ten years. It shall continue in force until notice of termination, to take effect two years thereafter, is given by either of the parties.
20. During the initial ten-year period, the undertaking and any treaty issuing therefrom may not be modified except by consent of both parties and with the approval of the General Assembly.
21. Any dispute relating to the application or the interpretation of the undertaking and any treaty issuing therefrom shall be referred, at the request of either party, to the international Court of Justice, unless the parties agree to another mode of settlement.
E. ASSETS
1. The movable assets of the Administration of Palestine shall be allocated to the Arab and Jewish States and the City of Jerusalem on an equitable basis. Allocations should be made by the United Nations Commission referred to in section B, paragraph 1, above. Immovable assets shall become the property of the government of the territory in which they are situated.
2. During the period between the appointment of the United Nations Commission and the termination of the Mandate, the mandatory Power shall, except in respect of ordinary operations, consult with the Commission on any measure which it may contemplate involving the liquidation, disposal or encumbering of the assets of the Palestine Government, such as the accumulated treasury surplus, the proceeds of Government bond issues, State lands or any other asset.
F. ADMISSION TO MEMBERSHIP IN THE UNITED NATIONS
When the independence of either the Arab or the Jewish State as envisaged in this plan has become effective and the declaration and undertaking, as envisaged in this plan, have been signed by either of them, sympathetic consideration should be given to its application for admission to membership in the United Nations in accordance with Article 4 of the Charter of the United Nations.
PART II
Boundaries5/
A. THE ARAB STATE
The area of the Arab State in Western Galilee is bounded on the west by the Mediterranean and on the north by the frontier of the Lebanon from Ras en Naqura to a point north of Saliha. From there the boundary proceeds southwards, leaving the built-up area of Saliha in the Arab State, to join the southernmost point of this village. Thence it follows the western boundary line of the villages of `Alma, Rihaniya and Teitaba, thence following the northern boundary line of Meirun village to join the Acre-Safad sub-district boundary line. It follows this line to a point west of Es Sammu'i village and joins it again at the northernmost point of Farradiya. Thence it follows the sub-district boundary line to the Acre-Safad main road. From here it follows the western boundary of Kafr I'nan village until it reaches the Tiberias-Acre sub-district boundary line, passing to the west of the junction of the Acre-Safad and Lubiya-Kafr I'nan roads. From south-west corner of Kafr I'nan village the boundary line follows the western boundary of the Tiberias sub-district to a point close to the boundary line between the villages of Maghar and Eilabun, thence bulging out to the west to include as much of the eastern part of the plain of Battuf as is necessary for the reservoir proposed by the Jewish Agency for the irrigation of lands to the south and east.
The boundary rejoins the Tiberias sub-district boundary at a point on the Nazareth-Tiberias road south-east of the built-up area of Tur'an; thence it runs southwards, at first following the sub-district boundary and then passing between the Kadoorie Agricultural School and Mount Tabor, to a point due south at the base of Mount Tabor. From here it runs due west, parallel to the horizontal grid line 230, to the north-east corner of the village lands of Tel Adashim. It then runs to the north-west corner of these lands, whence it turns south and west so as to include in the Arab State the sources of the Nazareth water supply in Yafa village. On reaching Ginneiger it follows the eastern, northern and western boundaries of the lands of this village to their south-west corner, whence it proceeds in a straight line to a point on the Haifa-Afula railway on the boundary between the villages of Sarid and El Mujeidil. This is the point of intersection.
The south-western boundary of the area of the Arab State in Galilee takes a line from this point, passing northwards along the eastern boundaries of Sarid and Gevat to the north-eastern corner of Nahalal, proceeding thence across the land of Kefar ha Horesh to a central point on the southern boundary of the village of `Ilut, thence westwards along that village boundary to the eastern boundary of Beit Lahm, thence northwards and north-eastwards along its western boundary to the north-eastern corner of Waldheim and thence north-westwards across the village lands of Shafa 'Amr to the south-eastern corner of Ramat Yohanan'. From here it runs due north-north-east to a point on the Shafa 'Amr-Haifa road, west of its junction with the road to I'Billin. From there it proceeds north-east to a point on the southern boundary of I'Billin situated to the west of the I'Billin-Birwa road. Thence along that boundary to its westernmost point, whence it turns to the north, follows across the village land of Tamra to the north-westernmost corner and along the western boundary of Julis until it reaches the Acre-Safad road. It then runs westwards along the southern side of the Safad-Acre road to the Galilee-Haifa District boundary, from which point it follows that boundary to the sea.
The boundary of the hill country of Samaria and Judea starts on the Jordan River at the Wadi Malih south-east of Beisan and runs due west to meet the Beisan-Jericho road and then follows the western side of that road in a north-westerly direction to the junction of the boundaries of the sub-districts of Beisan, Nablus, and Jenin. From that point it follows the Nablus-Jenin sub-district boundary westwards for a distance of about three kilometres and then turns north-westwards, passing to the east of the built-up areas of the villages of Jalbun and Faqqu'a, to the boundary of the sub-districts of Jenin and Beisan at a point north-east of Nuris. Thence it proceeds first north-westwards to a point due north of the built-up area of Zir'in and then westwards to the Afula-Jenin railway, thence north-westwards along the district boundary line to the point of intersection on the Hejaz railway. From here the boundary runs south-westwards, including the built-up area and some of the land of the village of Kh.Lid in the Arab State to cross the Haifa-Jenin road at a point on the district boundary between Haifa and Samaria west of El Mansi. It follows this boundary to the southernmost point of the village of El Buteimat. From here it follows the northern and eastern boundaries of the village of Ar'ara, rejoining the Haifa-Samaria district boundary at Wadi'Ara, and thence proceeding south-south-westwards in an approximately straight line joining up with the western boundary of Qaqun to a point east of the railway line on the eastern boundary of Qaqun village. From here it runs along the railway line some distance to the east of it to a point just east of the Tulkarm railway station. Thence the boundary follows a line half-way between the railway and the Tulkarm-Qalqiliya-Jaljuliya and Ras el Ein road to a point just east of Ras el Ein station, whence it proceeds along the railway some distance to the east of it to the point on the railway line south of the junction of the Haifa-Lydda and Beit Nabala lines, whence it proceeds along the southern border of Lydda airport to its south-west corner, thence in a south-westerly direction to a point just west of the built-up area of Sarafand el'Amar, whence it turns south, passing just to the west of the built-up area of Abu el Fadil to the north-east corner of the lands of Beer Ya'Aqov. (The boundary line should be so demarcated as to allow direct access from the Arab State to the airport.) Thence the boundary line follows the western and southern boundaries of Ramle village, to the north-east corner of El Na'ana village, thence in a straight line to the southernmost point of El Barriya, along the eastern boundary of that village and the southern boundary of 'Innaba village. Thence it turns north to follow the southern side of the Jaffa-Jerusalem road until El Qubab, whence it follows the road to the boundary of Abu Shusha. It runs along the eastern boundaries of Abu Shusha, Seidun, Hulda to the southernmost point of Hulda, thence westwards in a straight line to the north-eastern corner of Umm Kalkha, thence following the northern boundaries of Umm Kalkha, Qazaza and the northern and western boundaries of Mukhezin to the Gaza District boundary and thence runs across the village lands of El Mismiya, El Kabira, and Yasur to the southern point of intersection, which is midway between the built-up areas of Yasur and Batani Sharqi.
From the southern point of intersection the boundary lines run north-westwards between the villages of Gan Yavne and Barqa to the sea at a point half way between Nabi Yunis and Minat el Qila, and south-eastwards to a point west of Qastina, whence it turns in a south-westerly direction, passing to the east of the built-up areas of Es Sawafir, Es Sharqiya and Ibdis. From the south-east corner of Ibdis village it runs to a point south-west of the built-up area of Beit 'Affa, crossing the Hebron-El Majdal road just to the west of the built-up area of Iraq Suweidan. Thence it proceeds southwards along the western village boundary of El Faluja to the Beersheba sub-district boundary. It then runs across the tribal lands of 'Arab el Jubarat to a point on the boundary between the sub-districts of Beersheba and Hebron north of Kh. Khuweilifa, whence it proceeds in a south-westerly direction to a point on the Beersheba-Gaza main road two kilometres to the north-west of the town. It then turns south-eastwards to reach Wadi Sab' at a point situated one kilometre to the west of it. From here it turns north-eastwards and proceeds along Wadi Sab' and along the Beersheba-Hebron road for a distance of one kilometre, whence it turns eastwards and runs in a straight line to Kh. Kuseifa to join the Beersheba-Hebron sub-district boundary. It then follows the Beersheba-Hebron boundary eastwards to a point north of Ras Ez Zuweira, only departing from it so as to cut across the base of the indentation between vertical grid lines 150 and 160.
About five kilometres north-east of Ras ez Zuweira it turns north, excluding from the Arab State a strip along the coast of the Dead Sea not more than seven kilometres in depth, as far as Ein Geddi, whence it turns due east to join the Transjordan frontier in the Dead Sea.
The northern boundary of the Arab section of the coastal plain runs from a point between Minat el Qila and Nabi Yunis, passing between the built-up areas of Gan Yavne and Barqa to the point of intersection. From here it turns south-westwards, running across the lands of Batani Sharqi, along the eastern boundary of the lands of Beit Daras and across the lands of Julis, leaving the built-up areas of Batani Sharqi and Julis to the westwards, as far as the north-west corner of the lands of Beit Tima. Thence it runs east of El Jiya across the village lands of El Barbara along the eastern boundaries of the villages of Beit Jirja, Deir Suneid and Dimra. From the south-east corner of Dimra the boundary passes across the lands of Beit Hanun, leaving the Jewish lands of Nir-Am to the eastwards. From the south-east corner of Dimra the boundary passes across the lands of Beit Hanun, leaving the Jewish lands of Nir-Am to the eastwards. From the south-east corner of Beit Hanun the line runs south-west to a point south of the parallel grid line 100, then turns north-west for two kilometres, turning again in a south-westerly direction and continuing in an almost straight line to the north-west corner of the village lands of Kirbet Ikhza'a. From there it follows the boundary line of this village to its southernmost point. It then runs in a southernly direction along the vertical grid line 90 to its junction with the horizontal grid line 70. It then turns south-eastwards to Kh. el Ruheiba and then proceeds in a southerly direction to a point known as El Baha, beyond which it crosses the Beersheba-El 'Auja main road to the west of Kh. el Mushrifa. From there it joins Wadi El Zaiyatin just to the west of El Subeita. From there it turns to the north-east and then to the south-east following this Wadi and passes to the east of 'Abda to join Wadi Nafkh. It then bulges to the south-west along Wadi Nafkh. It then bulges to the south-west along Wadi Nafkh, Wadi Ajrim and Wadi Lassan to the point where Wadi Lassan crosses the Egyptian frontier.
The area of the Arab enclave of Jaffa consists of that part of the town-planning area of Jaffa which lies to the west of the Jewish quarters lying south of Tel-Aviv, to the west of the continuation of Herzl street up to its junction with the Jaffa-Jerusalem road, to the south-west of the section of the Jaffa-Jerusalem road lying south-east of that junction, to the west of Miqve Israel lands, to the north-west of Holon local council area, to the north of the line linking up the north-west corner of Holon with the north-east corner of Bat Yam local council area and to the north of Bat Yam local council area. The question of Karton quarter will be decided by the Boundary Commission, bearing in mind among other considerations the desirability of including the smallest possible number of its Arab inhabitants and the largest possible number of its Jewish inhabitants in the Jewish State.
B. THE JEWISH STATE
The north-eastern sector of the Jewish State (Eastern) Galilee) is bounded on the north and west by the Lebanese frontier and on the east by the frontiers of Syria and Transjordan. It includes the whole of the Hula Basin, Lake Tiberias, the whole of the Beisan sub-district, the boundary line being extended to the crest of the Gilboa mountains and the Wadi Malih. From there the Jewish State extends north-west, following the boundary described in respect of the Arab State.
The Jewish Section of the coastal plain extends from a point between Minat et Qila and Nabi Yunis in the Gaza sub-district and includes the towns of Haifa and Tel-Aviv, leaving Jaffa as an enclave of the Arab State. The eastern frontier of the Jewish State follows the boundary described in respect of the Arab State.
The Beersheba area comprises the whole of the Beersheba sub-district, including the Negeb and the eastern part of the Gaza sub-district, but excluding the town of Beersheba and those areas described in respect of the Arab State. It includes also a strip of land along the Dead Sea stretching from the Beersheba-Hebron sub-district boundary line to Ein Geddi, as described in respect of the Arab State.
C. THE CITY OF JERUSALEM
The boundaries of the City of Jerusalem are as defined in the recommendations on the City of Jerusalem. (See Part III, Section B, below).
PART III
City of Jerusalem
A. SPECIAL REGIME
The City of Jerusalem shall be established as a corpus separatum under a special international regime and shall be administered by the United Nations. The Trusteeship Council shall be designated to discharge the responsibilities of the Administering Authority on behalf of the United Nations.
B. BOUNDARIES OF THE CITY
The City of Jerusalem shall include the present municipality of Jerusalem plus the surrounding villages and towns, the most eastern of which shall be Abu Dis; the most southern, Bethlehem; the most western, Ein Karim (including also the built-up area of Motsa); and the most northern Shu'fat, as indicated on the attached sketch-map (annex B).
C. STATUTE OF THE CITY
The Trusteeship Council shall, within five months of the approval of the present plan, elaborate and approve a detailed Statute of the City which shall contain inter alia the substance of the following provisions:
1. Government machinery; special objectives. The Administering Authority in discharging its administrative obligations shall pursue the following special objectives:
(a) To protect and to preserve the unique spiritual and religious interests located in the city of the three great monotheistic faiths throughout the world, Christian, Jewish and Moslem; to this end to ensure that order and peace, and especially religious peace, reign in Jerusalem;
(b) To foster co-operation among all the inhabitants of the city in their own interests as well as in order to encourage and support the peaceful development of the mutual relations between the two Palestinian peoples throughout the Holy Land; to promote the security, well-being and any constructive measures of development of the residents, having regard to the special circumstances and customs of the various peoples and communities.
2. Governor and administrative staff. A Governor of the City of Jerusalem shall be appointed by the Trusteeship Council and shall be responsible to it. He shall be selected on the basis of special qualifications and without regard to nationality. He shall not, however, be a citizen of either State in Palestine.
The Governor shall represent the United Nations in the City and shall exercise on their behalf all powers of administration, including the conduct of external affairs. He shall be assisted by an administrative staff classed as international officers in the meaning of Article 100 of the Charter and chosen whenever practicable from the residents of the city and of the rest of Palestine on a non-discriminatory basis. A detailed plan for the organization of the administration of the city shall be submitted by the Governor to the Trusteeship Council and duly approved by it.
3. Local autonomy. (a) The existing local autonomous units in the territory of the city (villages, townships and municipalities) shall enjoy wide powers of local government and administration.
(b) The Governor shall study and submit for the consideration and decision of the Trusteeship Council a plan for the establishment of a special town units consisting respectively, of the Jewish and Arab sections of new Jerusalem. The new town units shall continue to form part of the present municipality of Jerusalem.
4. Security measures. (a) The City of Jerusalem shall be demilitarized; its neutrality shall be declared and preserved, and no para-military formations, exercises or activities shall be permitted within its borders.
(b) Should the administration of the City of Jerusalem be seriously obstructed or prevented by the non-co-operation or interference of one or more sections of the population, the Governor shall have authority to take such measures as may be necessary to restore the effective functioning of the administration.
(c) To assist in the maintenance of internal law and order and especially for the protection of the Holy Places and religious buildings and sites in the city, the Governor shall organize a special police force of adequate strength, the members of which shall be recruited outside of Palestine. The Governor shall be empowered to direct such budgetary provision as may be necessary for the maintenance of this force.
5. Legislative organization. A Legislative Council, elected by adult residents of the city irrespective of nationality on the basis of universal and secret suffrage and proportional representation, shall have powers of legislation and taxation. No legislative measures shall, however, conflict or interfere with the provisions which will be set forth in the Statute of the City, nor shall any law, regulation, or official action prevail over them. The Statute shall grant to the Governor a right of vetoing bills inconsistent with the provisions referred to in the preceding sentence. It shall also empower him to promulgate temporary ordinances in case the council fails to adopt in time a bill deemed essential to the normal functioning of the administration.
6. Administration of justice. The Statute shall provide for the establishment of an independent judiciary system, including a court of appeal. All the inhabitants of the City shall be subject to it.
7. Economic union and economic regime. The City of Jerusalem shall be included in the Economic Union of Palestine and be bound by all stipulations of the undertaking and of any treaties issued therefrom, as well as by the decision of the Joint Economic Board. The headquarters of the Economic Board shall be established in the territory of the City.
The Statute shall provide for the regulation of economic matters not falling within the regime of the Economic Union, on the basis of equal treatment and non-discrimination for all members of the United Nations and their nationals.
8. Freedom of transit and visit; control of residents. Subject to considerations of security, and of economic welfare as determined by the Governor under the directions of the Trusteeship Council, freedom of entry into, and residence within, the borders of the City shall be guaranteed for the residents or citizens of the Arab and Jewish States. Immigration into, and residence within, the borders of the city for nationals of other States shall be controlled by the Governor under the directions of the Trusteeship Council.
9. Relations with the Arab and Jewish States. Representatives of the Arab and Jewish States shall be accredited to the Governor of the City and charged with the protection of the interests of their States and nationals in connexion with the international administration of the City.
10. Official languages. Arabic and Hebrew shall be the official languages of the city. This will not preclude the adoption of one or more additional working languages, as may be required.
11. Citizenship. All the residents shall become ipso facto citizens of the City of Jerusalem unless they opt for citizenship of the State of which they have been citizens or, if Arabs or Jews, have filed notice of intention to become citizens of the Arab or Jewish State respectively, according to part I, section B, paragraph 9, of this plan.
The Trusteeship Council shall make arrangements for consular protection of the citizens of the City outside its territory.
12. Freedoms of Citizens. (a) Subject only to the requirements of public order and morals, the inhabitants of the City shall be ensured the enjoyment of human rights and fundamental freedoms, including freedom of conscience, religion and worship, language, education, speech and press, assembly and association, and petition.
(b) No discrimination of any kind shall be made between the inhabitants on the grounds of race, religion, language or sex.
(c) All persons within the City shall be entitled to equal protection of the laws.
(d) The family law and personal status of the various persons and communities and their religious interests, including endowments, shall be respected.
(e) Except as may be required for the maintenance of public order and good government, no measure shall be taken to obstruct or interfere with the enterprise of religious or charitable bodies of all faiths or to discriminate against any representative or member of these bodies on the ground of his religion or nationality.
(f) The City shall ensure adequate primary and secondary education for the Arab and Jewish communities respectively, in their own languages and in accordance with their cultural traditions.
The right of each community to maintain its own schools for the education of its own members in its own language, while conforming to such educational requirements of a general nature as the City may impose, shall not be denied or impaired. Foreign educational establishments shall continue their activity on the basis of their existing rights.
(g) No restriction shall be imposed on the free use by any inhabitant of the City of any language in private intercourse, in commerce, in religion, in the Press or in publications of any kind, or at public meetings.
13. Holy Places. (a) Existing rights in respect of Holy Places and religious buildings or sites shall not be denied or impaired.
(b) Free access to the Holy Places and religious buildings or sites and the free exercise of worship shall be secured in conformity with existing rights and subject to the requirements of public order and decorum.
(c) Holy Places and religious buildings or sites shall be preserved. No act shall be permitted which may in any way impair their sacred character. If at any time it appears to the Governor that any particular Holy Place, religious building or site is in need of urgent repair, the Governor may call upon the community or communities concerned to carry out such repair. The Governor may carry it out himself at the expense of the community or communities concerned if no action is taken within a reasonable time.
(d) No taxation shall be levied in respect of any Holy Place, religious building or site which was exempt from taxation on the date of the creation of the City. No change in the incidence of such taxation shall be made which would either discriminate between the owners or occupiers of Holy Places, religious buildings or sites, or would place such owners or occupiers in a position less favourable in relation to the general incidence of taxation than existed at the time of the adoption of the Assembly's recommendations.
14. Special powers of the Governor in respect of the Holy Places, religious buildings and sites in the City and in any part of Palestine. (a) The protection of the Holy Places, religious buildings and sites located in the City of Jerusalem shall be a special concern of the Governor.
(b) With relation to such places, buildings and sites in Palestine outside the city, the Governor shall determine, on the ground of powers granted to him by the Constitutions of both States, whether the provisions of the Constitutions of the Arab and Jewish States in Palestine dealing therewith and the religious rights appertaining thereto are being properly applied and respected.
(c) The Governor shall also be empowered to make decisions on the basis of existing rights in cases of disputes which may arise between the different religious communities or the rites of a religious community in respect of the Holy Places, religious buildings and sites in any part of Palestine.
In this task he may be assisted by a consultative council of representatives of different denominations acting in an advisory capacity.
D. DURATION OF THE SPECIAL REGIME
The Statute elaborated by the Trusteeship Council on the aforementioned principles shall come into force not later than 1 October 1948. It shall remain in force in the first instance for a period of ten years, unless the Trusteeship Council finds it necessary to undertake a re-examination of these provisions at an earlier date. After the expiration of this period the whole scheme shall be subject to re-examination by the Trusteeship Council in the light of the experience acquired with its functioning. The residents of the City shall be then free to express by means of a referendum their wishes as to possible modifications of the regime of the City.
PART IV
CAPITULATIONS
States whose nationals have in the past enjoyed in Palestine the privileges and immunities of foreigners, including the benefits of consular jurisdiction and protection, as formerly enjoyed by capitulation or usage in the Ottoman Empire, are invited to renounce any right pertaining to them to the re-establishment of such privileges and immunities in the proposed Arab and Jewish States and the City of Jerusalem.
* * *
Notes
1/ See Official Records of the second session of the General Assembly, Supplement No. 11, Volumes I-IV.
2/ This resolution was adopted without reference to a Committee.
3/ The following stipulation shall be added to the declaration concerning the Jewish State: "In the Jewish State adequate facilities shall be given to Arab-speaking citizens for the use of their language, either orally or in writing, in the legislature, before the Courts and in the administration."
4/ In the declaration concerning the Arab State, the words "by an Arab in the Jewish State" should be replaced by the words "by a Jew in the Arab State".
5/ The boundary lines described in part II are indicated in Annex A. The base map used in marking and describing this boundary is "Palestine 1:250000" published by the Survey of Palestine, 1946.
Annex A
Plan of Partition with Economic Union
Annex B
City of Jerusalem
Boundaries Proposed By The Ad Hoc Committee On The Palestinian Question
* *** *
UNISPAL note
Voting as per publication "The Origins and Evolution of the Palestine Problem:
1917-1988":Database 'UNISPAL', View 'Documents bydate', Document 'The Origins and Evolution of the Palestine Problem: 1917-1988 - DPR study, part II: 1947-1977', Anchor 'In favour: Australia, Belgium, B'